What might be some of the causes and consequences of industrial concentration? Provide some examples
What will be an ideal response?
Some industries are more concentrated than others because of technical properties of their production technologies or unique characteristics of the markets they serve. Economies of scale, which allow firms to reduce their average costs as they increase their rates of output, favor large-scale production over small-scale production. Thus, industries for which scale economies are important (e.g., auto manufacturing and petroleum refining) are expected to be more concentrated than others in which costs do not fall as rapidly as output expands (e.g., cut-and-sew apparel manufacturing). Similarly, concentration tends to be higher in industries, such as aircraft and semiconductor manufacturing, where learning curves generate substantial production-cost savings as additional units of the original model or design are made.
You might also like to view...
The chaebols encouraged the Korean government to open up Korean financial markets to foreign capital. The Korean government responded by
A) allowing unlimited short-term foreign borrowing but maintained quantity restrictions on long-term foreign borrowing by financial institutions. B) allowing unlimited short-term and long-term foreign borrowing by financial institutions. C) maintaining quantity restrictions on short-term foreign borrowing but allowing unlimited long-term foreign borrowing by financial institutions. D) not allowing any foreign borrowing by financial institutions.
Why does the government not have to repay debt, as do private individuals?
A. Because the government can ignore creditors and refuse payment. B. Because the government, as a dictatorship, is unresponsive to demands for repayment. C. Because the government has no debt; it owes it to itself. D. Because the government does not have a finite life, as do individuals.
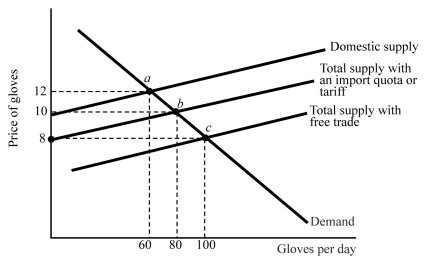
 Refer to Figure 18.1. With free trade, what is the equilibrium quantity of gloves in Duckland?
Refer to Figure 18.1. With free trade, what is the equilibrium quantity of gloves in Duckland?
A. 100 B. 80 C. 60 D. 40
Assuming price elasticity of demand is reported as an absolute value, an elastic demand has an elasticity:
A. greater than one. B. greater than zero and less than one. C. exactly one. D. less than one.