I) The growth rate of Eduland's money supply in a particular year was 8.5%
What was the growth rate of real GDP if the inflation rate in the same year was 4%?
ii) What is likely to happen if the growth rate of money supply doubles in the following year, while the growth rate of real output remains unchanged?
i) According to the quantity theory of money, the ratio of money supply to nominal GDP is constant. Therefore, the rate of growth of money supply must equal the rate of growth of nominal GDP. However, growth rate of nominal GDP is the sum of growth rate of real GDP and the inflation rate. Thus,
Rate of Growth in Money Supply = Rate of Growth in Real GDP + Inflation Rate. Thus, the growth rate of real GDP in this case is 8.5% - 4% = 4.5%.
ii) If the growth rate of money supply doubles in the following year and the growth rate of real output remains unchanged, the inflation rate will also double.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the below graphs. (Assume that the pre-migration labor force in Country A is 0d and that it is 0u in country B.) If business income is total output minus total labor cost, then business income in country A after the immigration occurs is equal to area:
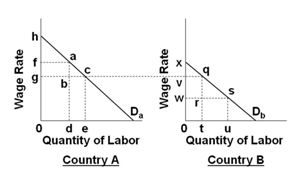
A. haf
B. habg
C. hcg
D. hce0
The main reason people hold money is that
A) money is intrinsically valuable. B) money is used to buy goods and services. C) money is power. D) money provides a standard of value.
One requirement for an effective nominal anchor is ________
A) price stability B) credibility C) fixed exchange rates D) rational expectations
Refer to the above figure. What price-output combination would apply under perfect competition?
A) P4 and Q1 B) P3 and Q2 C) P2 and Q3 D) P1 and Q1