Discuss how the interdependence of input markets for labor, capital, and land might affect supply, demand, and wages or rental prices.
What will be an ideal response?
Because these markets are interdependent, supply, demand, and wages or prices
might move the curves in other input markets. For example, if wages are above the
equilibrium, an employer might substitute machines for some human workers to reduce
costs. This would send unemployed workers into the market, increasing the supply of
available labor and moving the supply curve to the right. With more workers in the
market for jobs, workers might be willing to supply their labor services for an amount lower than the prevailing wage. Similarly, if capital costs rise dramatically, then owners
might scale back the use of some equipment and consequently reduce their
employment of the human operators of the equipment. If capital costs begin to fall, then
there might be an increase again in demand for workers to operate machinery. In a
different scenario, when capital costs rise, the business owners might switch from
automation to more labor-intensive production methods and hire more workers if the
cost of the additional wages is less than the previous capital costs.
You might also like to view...
Rent controls and controls on other prices often aggravate the very problem they are intended to solve.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
For a perfectly competitive firm, marginal revenue is
A) less than the price. B) greater than the price. C) equal to the price. D) equal to the change in profit from selling one more unit. E) undefined because the firm's demand curve is horizontal.
Monopolistic competition means
A) monopolies from several countries compete in the global market. B) a large number of firms producing homogeneous products. C) a large number of firms producing differentiated products. D) few firms producing differentiated products.
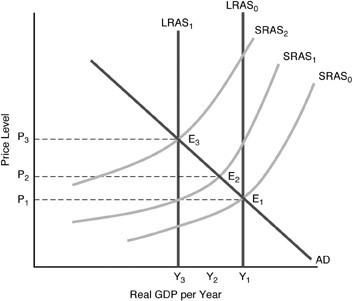 In the above figure, starting at E3, if there is an increase in technology that causes a permanent increase in production capabilities
In the above figure, starting at E3, if there is an increase in technology that causes a permanent increase in production capabilities
A. aggregate supply would shift to SRAS1 and LRAS0 would shift to LRAS1. B. aggregate supply would shift to SRAS0 and LRAS1 would shift to LRAS0. C. aggregate supply would shift to SRAS1 and then return to SRAS0. D. aggregate supply would shift to SRAS2 and LRAS0 would shift to LRAS1.