Increasing cost industries are consistent with ________ in the long run.
A. the law of supply
B. the law of diminishing marginal product
C. the law of demand
D. None of these are correct.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Since it is a centrally planned economy, China does not face opportunity costs when economic decisions are made.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Suppose we live in an exchange economy with two goods. I own 50 of both goods, and you own 250 of both goods. My tastes are captured by the utility function 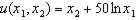
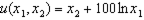
c. Suppose the government transfers 100 units of your good 1 endowment to me. How is your answer to (a) and (b) affected? d. Suppose the government instead transfers 100 units of good 2 from you to me. How is your answer to (a) and (b) affected? e. Do you think your answers to (c) and (d) generally hold for most types of tastes -- or do you think they arise because of some specific feature of these tastes? What will be an ideal response?
Refer to Table 19-17. What is real GDP in 2016, using 2011 as the base year?
A) $3,320 B) $3,690 C) $6,360 D) $7,035
If factor prices decrease:
a) a firm will move down along its long-run average cost curve only. b) a firm will move down along both its long-run and short-run average cost curves. c) both the long-run and short-run average cost curves will shift downward. d) there will be no change in the cost curves in the long run. e) there will be a downward shift in the long-run average cost curve but not in the short-run average cost curve.