Explain why the economic analysis of monopolistic competition is so complex
What will be an ideal response?
The model of the monopolistic ally competitive firm as presented in this chapter is a simplification of a great deal of complexity that is found in this market structure. The monopolistic ally competitive firm has some control over the three factors (price, product, and promotion) but there are many combinations of these factors for a particular firm. The model of the representative firm in monopolistic competition does not take into account all the combinations or all the degrees to which these factors can be changed. In addition, the basic model also does not take into account how rivals will react to changes in any one of the factors.
You might also like to view...
A woman who decides to drive to work rather than take the bus
A) is wasting scarce resources. B) is behaving inefficiently. C) thinks driving is more economically efficient for her. D) is probably paying attention to personal comfort and convenience rather than economic efficiency.
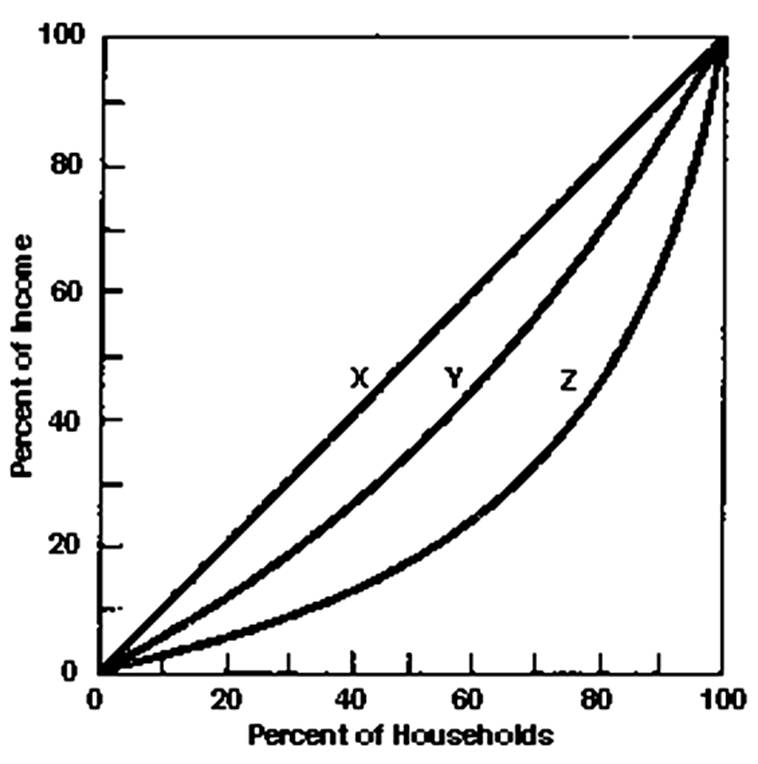
What is the percentage of income received by the upper quintile on line Z?
The model predicts that a temporary increase in government purchases causes:
a. an increase in consumption. b. a reduction in gross investment. c. a reduction in real GDP. d. all of the above.
It has been proposed that a government agency be charged with the task of determining the amount of pollution that the atmosphere (or a body of water) can safely absorb, establish "rights" to this limited amount of pollution, and sell those limited amount of rights to firms. The firms can then buy and sell these rights among themselves later. This approach is known as the:
A. Taxes and subsidies system B. Cap and trade system C. Property rights system D. Market and command system