Refer to the diagram, where S d and D d are the domestic supply and demand for a product and P c is the world price of that product. S d + Q is the product supply curve after an import quota is imposed. Assuming there is no tariff, the import quota:
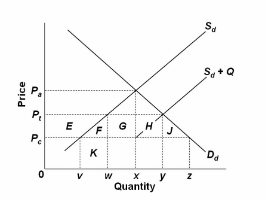
A. will increase U.S. Treasury revenue by areas G + H.
B. will increase U.S. Treasury revenue by areas E + F + G + H + J.
C. may either increase or decrease the total revenues of foreign producers, depending on the elasticity of domestic demand.
D. will increase the revenues of foreign firms by area E.
C. may either increase or decrease the total revenues of foreign producers, depending on the elasticity of domestic demand.
You might also like to view...
What is a downside of trade protection?
a. Instead of protecting U.S. interests and giving domestic manufacturing an advantage over items manufactured elsewhere, it can have the unintended effect of driving the manufacturing completely out of the country. b. It can give U.S. interests and domestic manufacturing too much of an advantage over items manufactured elsewhere, having the unintended effect of driving the manufacturing completely out of the country. c. It can give U.S. interests and domestic manufacturing too much of an advantage over items manufactured elsewhere, having the unintended effect of bringing more manufacturing into the country than can be handled. d. Instead of protecting U.S. interests and giving domestic manufacturing an advantage over items manufactured elsewhere, it can have the unintended effect of bringing more manufacturing into the country than can be handled.
When a government splits a natural monopoly vertically, it is breaking the company up:
A. along its stages of production. B. in order to maximize its profits. C. into smaller companies providing the same goods. D. in order to capture all efficiencies possible.
Each C + I + G + (X ? IM) expenditure schedule is drawn assuming a specific
A. income level. B. spending level. C. production level. D. price level.
A government policy of providing free public education is an example of a policy to promote economic growth by:
A. increasing the availability of natural resources. B. increasing physical capital. C. improving technology. D. increasing human capital.