A stainless steel pin fin 5-cm-long, 6-mm-OD, extends from a flat plate into a 175 m/s air stream as shown in the sketch. Estimate (a) the average heat transfer coefficient between air and the fin. (b) the temperature at the end of the fin. (c) the rate of heat flow from the fin.
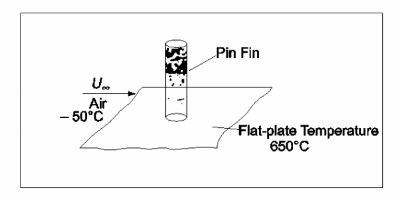
GIVEN
• A stainless steel pin fin in an air stream
• Pin length (L) = 5 cm = 0.05 m
• Pin diameter (D) = 6 mm = 0.006 m
• Air velocity (U?) = 175 m/s FIND
(a) The average heat transfer coefficient ( h c) (b) The temperature of the end of the fin (TL) (c) The rate of heat flow from the fin (qf)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Air approaching the fin has negligible turbulence
• Radiative heat transfer is negligible
• Steel is type 304
• Steel properties are uniform
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0202 W/(m K) Kinematic viscosity (?) = 9.3 × 10–6 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 From Appendix 2, Table 10, for Type 304 stainless steel ks = 14.4 W/(m K) at 20°C (Note that figure 1.6 shows very little increase in k for stainless steel in the range of 300°C to 700°C.)
(a) The Reynolds number is
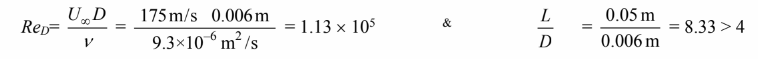
Therefore, may be used. (Note that Pr/Prs = 1)
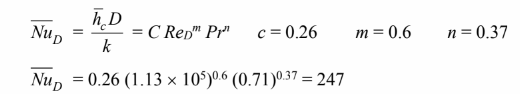
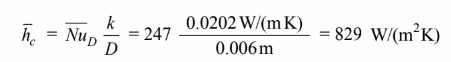
(b) for a fin of uniform cross-section with convection at the tip, the temperature
distribution is
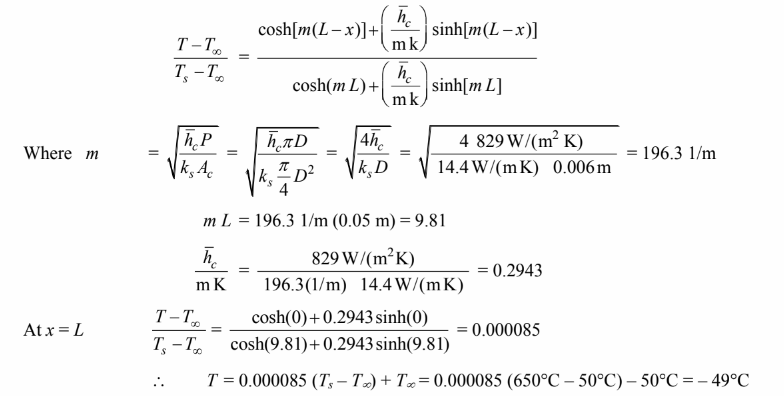
The tip temperature is practically the same as the ambient temperature.
(c) The rate of heat transfer is.
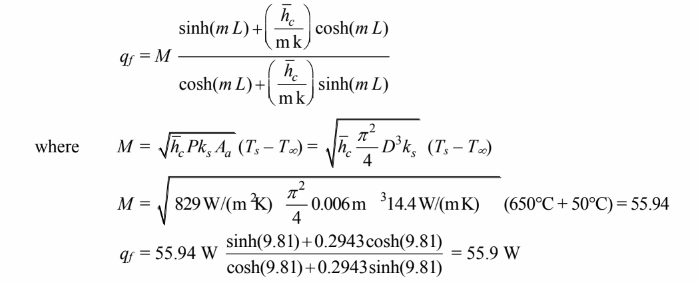
COMMENTS
These results should be considered an estimate due to uncertainty in the air properties.
Also, due to the presence of the surface from which the fin protrudes, the flow is not uniform as
assumed by Equation (6.3), therefore, the heat transfer coefficient may vary.
You might also like to view...
Air with a density of 1.20 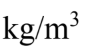 flows through a 75.0 cm diameter pipe with a velocity of 2.00 m/s. What is the mass flow rate?
flows through a 75.0 cm diameter pipe with a velocity of 2.00 m/s. What is the mass flow rate?
A. 0.95 kg/s B. 1.06 kg/s C. 1.20 kg/s D. 1.26 kg/s E. 1.48 kg/s
A star can remain in the giant-star stage for about 90 percent of its total lifetime before it dies
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
A merger between two large galaxies of comparable size will most likely produce:
A) two small elliptical galaxies. B) a large elliptical galaxy. C) a small elliptical galaxy and a small spiral galaxy. D) a large spiral galaxy. E) a small elliptical galaxy and a large spiral galaxy.
Compton Scattering: A certain photon, after being scattered from a free electron that was at rest, moves at an angle of 120° with respect to the incident direction. If the wavelength of the incident photon is 0.6110 nm, what is the kinetic energy of the recoiling electron? (melectron = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ? s)
A. 1.5 × 10-18 J B. 1.9 × 10-18 J C. 3.1 × 10-18 J D. 4.3 × 10-18 J E. 5.2 × 10-18 J