The enzyme that covalently links both strands of a vector and inserted DNA in molecular cloning is
A) DNA ligase.
B) DNA phosphatase.
C) DNA hydrolase.
D) DNA transferase.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Albinism is a recessive disorder in which the skin and hair fail to produce pigment. The following question(s) ask you to evaluate the pedigree chart shown here in which "N" is the allele for normal pigmentation and "n" is the allele for albinism. The shaded circles for Deirdre and Shannon represent the only individuals expressing the disorder.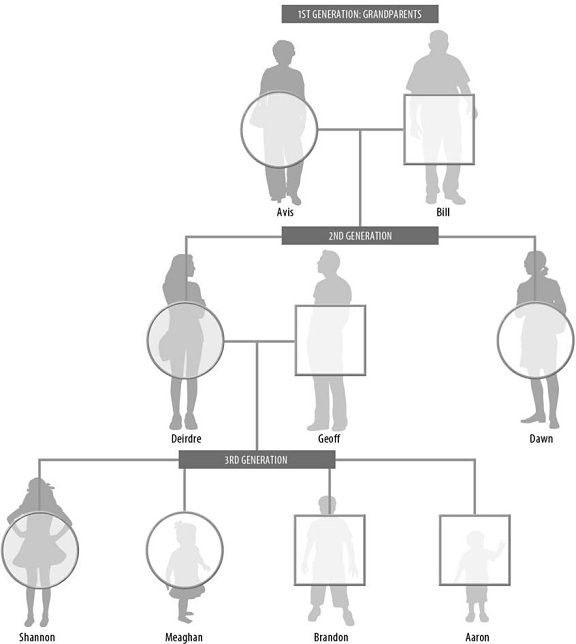 What is Deirdre's phenotype?
What is Deirdre's phenotype?
A. Normal B. nn C. Albino D. Cannot be determined
Vanillin is to flavonoids as atropine is to
A. flavonoids. B. terpenoids. C. polyketides. D. alkoloids. E. B-carotenes.
Who would have larger numbers of bacteria living on the surface of their skin, a person living in the tropics or in the desert, and why?
A. The tropics would provide more shade, so the surface of the skin wouldn't be exposed to high levels of ultraviolet radiation. This would protect the bacteria on the skin, and they would have higher numbers due to this shading effect. B. The very low humidity of the desert would lead to rapid evaporation of sweat and sebum from an individual's skin. Bacteria need these secretions for a nutrient source. Without them, bacteria would be found in much lower numbers on the skin of a person in the desert than the skin of the person in the tropics. C. The constant secretion (and lack of evaporation) of high amounts of sweat would produce a highly salty environment on the skin of a person in the tropics. This would provide a local environment that would be too hostile for microbes to survive, so the number of microbes on the skin of the person in the tropics would be lower than that of the person in the desert. D. The constant secretion of large amounts of sweat would wash bacteria off of the skin of the person in the tropics. As such, the person in the desert should have much more bacteria on their skin than the person in the tropics would.
The most diverse, successful, and familiar group of plants today are the:a
gymnosperms. b. bryophytes. c. ferns. d. angiosperms. e. lycopods.