Suppose the Swiss government subsidized its watch-making industry, enabling Swiss producers to undersell foreign watch producers. The law of comparative advantage indicates that watch-importing nations would best take advantage of the Swiss subsidization policy by
a. setting a tariff high enough to just offset the subsidy granted to the Swiss watch-making industry
b. setting a declining quota on the import of Swiss watches such that the nation's domestic watch-making industry would continue to grow at the same rate as the rest of the economy.
c. setting a tariff such that the prices of Swiss and domestic watches to the consumer are equal.
d. gladly accepting the subsidy of the Swiss government, making the appropriate adjustment for the resources temporarily displaced from the domestic watch-making industry.
d
You might also like to view...
The economy pictured in the figure has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 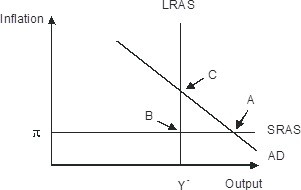
A. recessionary; A B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; B D. expansionary; A
"Medium term notes" have a maturity ranging up to
A) one year. B) two years. C) five years. D) ten years.
Figure (a) represents the domestic demand and supply of televisions. Suppose free trade is allowed and the current world price of televisions is P1 as shown in Figure (b). Now suppose the domestic government imposes a tariff increasing the domestic price to P2 in Figure (b). This tariff will cause
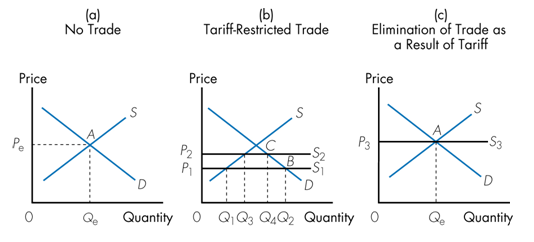
a. imports to fall from Q2 minus Q1 to Q4 minus Q3.
b. domestic producers to increase their production from Q1 to Q3.
c. domestic consumers to reduce their consumption from Q2 to Q4.
d. All of the above.
A monopoly may arise due to:
A. a patent. B. network externalities. C. large economies of scale. D. All of these