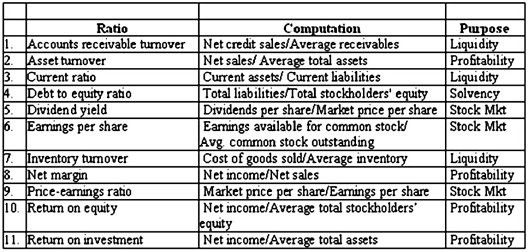
Ratios can be used for different purposes. For example, a variety of ratios have been developed to assess a firm's liquidity. Similarly, ratios have been developed to assess solvency, profitability, and stock market strength. A sample of commonly used ratios for these purposes is provided in the table below.Required:In the middle column of the table, provide the formula to compute the specified ratio. In the final column, indicate the purpose (Liquidity, Solvency, Profitability, and Stock market strength) for which the ratio is most commonly used. The first item is completed as an example.
What will be an ideal response?
You might also like to view...
The income statement of Hope Market, Inc reported a gain from the sale of land. How are the cash flow effects of this transaction reported on the statement of cash flows if the direct method is used to prepare the Operating Activities category?
a. The entire proceeds from the sale of the land are reported as an investing activity. b. The gain on the sale of land is reported in the Investing Activities category as a cash flow from the sale of land. c. The entire proceeds from the sale of the land are reported as an operating activity. d. The cash received from the sale of land is reported in the financing activity category as a cash flow from the sale of land.
Which of the following statements characterizes defined contribution plans?
a. They are more complex in construction than defined benefit plans. b. The employer's obligation is satisfied by making the appropriate amount of periodic contribution. c. The investment risk is borne by the employer. d. Contributions are made in equal amounts by employer and employees.
An increase in the accounts receivable turnover may be due to an improvement in the collection of receivables or to a change in the granting of credit and/or in collection practices
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
At the end of the fiscal year, the balance in Factory Overhead is small. This balance would normally be:
A) transferred to Work in Process B) transferred to Cost of Goods Sold C) transferred to Finished Goods D) allocated between Work in Process and Finished Goods