How much is saving when disposable income is $1600 billion?
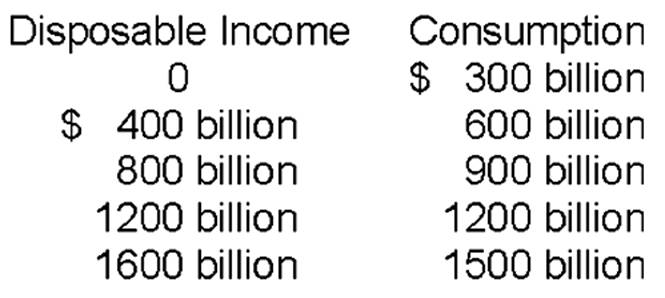
$100 billion
You might also like to view...
Since 1974, commercial banks importance as a source of funds for nonfinancial borrowers
A) has shrunk dramatically, from around 40 percent of total credit advanced to around 25 percent by 2014. B) has shrunk dramatically, from around 70 percent of total credit advanced to below 50 percent by 2014. C) has expanded dramatically, from around 50 percent of total credit advanced to above 70 percent by 2014. D) has expanded dramatically, from around 30 percent of total credit advanced to above 50 percent by 2014.
In the 1960s and 1970s, research funding by the U.S. government and some universities led to revolutionary advances in network computing
These advances in communication and network technology remained largely isolated to governmental and academic use. By the mid-to-late 1990s, the Internet began to be widely adopted with massive increases in productivity (which journalists dubbed the "new economy"). Which of the following is an appropriate description of the mechanism behind this supply shock? A) Since this "new economy" was a new paradigm, the transition from a pre-internet to an internet economy was initially costly. Thus, the AS curve likely shifted to the left and unemployment likely increased in the short-run. B) The ensuing increase in productive capacity led to the rightward shift of the LRAS which is a likely explanation for the protracted decline in the unemployment rate of the 1990s. C) A negative output gap would have resulted in the short-run, but it was eventually closed by a rightward shift of the LRAS which is a likely explanation for the protracted decline in the inflation rate of the 1990s. D) all of the above E) none of the above
A company's computer is classified as what account type:
a. Expense b. Owner's Equity c. Fixed Asset d. Retained Earnings
A situation in which output decreases while prices increase is often referred to as:
A. inflation. B. negative economic growth. C. a recession. D. stagflation.