Is there any common characteristic shared by government-inhibited goods and government-sponsored goods? Explain briefly
What will be an ideal response?
Government-inhibited and government-sponsored goods do not have any inherent characteristics that qualify them as such; instead, through the political process, people collectively make judgments about which goods and services are "good" for society and which are "bad."
You might also like to view...
The figure below shows the supply and demand curves for oranges in Smallville. 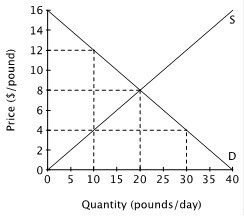 At the price of $4 per pound, sellers offer ________ pounds of oranges per day, and buyers want to purchase ________ pounds of oranges a day.
At the price of $4 per pound, sellers offer ________ pounds of oranges per day, and buyers want to purchase ________ pounds of oranges a day.
A. 30; 10 B. 20; 20 C. 10; 20 D. 10; 30
Which of the following countries experienced the sharpest fiscal contraction in order to gain admission to the Euro club?
A) Portugal B) Spain C) Italy D) France
The profit-maximizing number of workers for a monopsony to employ is derived at the point where the marginal revenue product of labor is equal to the marginal factor cost of labor
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Suppose we were analyzing the pound per Swiss franc foreign exchange market. If there is the expectation that the Swiss franc will rise in value in the near future, then in the spot market:
a. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market falls, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market falls, causing an uncertain change in the value of the Swiss franc. b. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market falls, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, causing an appreciation of the Swiss franc. c. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, causing an uncertain change in the value of the Swiss franc. d. The supply of Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market rises, and the demand for Swiss francs in the foreign exchange market falls, causing a depreciation of the Swiss franc. e. Neither supply nor demand in the foreign exchange market change because relative international prices influence trade flows and not the exchange rate.