A long solenoid (n = 80 turns/cm) carries a current of 70 mA. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic field inside the solenoid
7.0 gauss
You might also like to view...
Two experimental runs are performed to determine the calorimetric properties of an alcohol which has a melting point of -10.0° C
In the first run, a 200-g cube of frozen alcohol, at the melting point, is added to 300 g of water at 20.0°C in a styrofoam container. When thermal equilibrium is reached, the alcohol-water solution is at a temperature of 5.0°C. In the second run, an identical cube of alcohol is added to 500 g of water at 20.0°C and the temperature at thermal equilibrium is 10.0°C. The specific heat capacity of water is 4190 J/kg ? K. Assume no heat is exchanged with the styrofoam container and the surroundings. What is the heat of fusion of the alcohol? A) 7.1 × 104 J/kg B) 7.9 × 104 J/kg C) 5.5 × 104 J/kg D) 6.3 × 104 J/kg E) 8.7 × 104 J/kg
Increasing the amplitude of a mass-and-spring system causes what kind of change in the resonant frequency of the system? (Assume no other changes in the system.)
A) The frequency increases. B) The frequency decreases. C) There is no change in the frequency. D) The frequency depends on the displacement, not the amplitude.
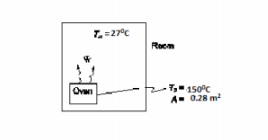
A small oven with a surface area of 0.28 m2 is located in a room in which the walls and the air are at a temperature of 27°C. The exterior surface of the oven is at 150°C and the net heat transfer by radiation between the oven’s surface and the surroundings is 586 W. If the average convective heat transfer coefficient between the oven and the surrounding air is 11 W/(m2 K), calculate: (a) the net heat transfer between the oven and the surroundings in W, (b) the thermal resistance at the surface for radiation and convection, respectively, in K/W, and (c) the combined heat transfer coefficient in W/(m2 K).
GIVEN

FIND

ASSUMPTIONS
- Steady state prevails
SKETCH
Free Fall: A toy rocket is launched vertically from ground level at time t = 0 s. The rocket engine provides constant upward acceleration during the burn phase. At the instant of engine burnout, the rocket has risen to 49.0 m and acquired an upward velocity of 60.0 m/s. The rocket continues to rise with insignificant air resistance in unpowered flight, reaches maximum height, and falls back to the ground. The maximum height reached by the rocket is closest to
A. 233 m. B. 221 m. C. 209 m. D. 244 m. E. 256 m.