Which one of the following is not true?
a. An exchange rate is the price of one currency in terms of another.
b. An exchange rate is the means by which the price of a good in one country is translated into the price to the buyer in another country.
c. The cost of a foreign good in dollars will depend on the current exchange rate.
d. The exchange rate will affect the willingness of foreign buyers and sellers to trade with each other.
e. The exchange rate is the price of a currency in terms of another currency for exchanges of goods and services but not for financial transactions.
E
You might also like to view...
The payoff matrix below shows the daily profit for two firms, Row Restaurant and Column Cafe, for two different strategies, publishing coupons in the student paper and not publishing coupons in the student paper. 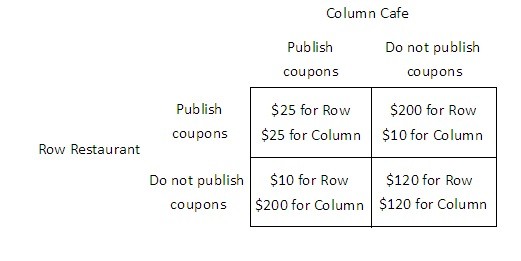 If Row Restaurant publishes coupons, Column Cafe would earn the highest profit if it:
If Row Restaurant publishes coupons, Column Cafe would earn the highest profit if it:
A. did not publish coupons. B. chooses either strategy because Column Cafe will have the same profit in either case. C. also published coupons. D. only offered coupons half of the time.
The law of large numbers allows insurance companies to
A) hold capital market instruments as assets without fearing overly large numbers of defaults. B) hold money market instruments as assets without fearing overly large numbers of defaults. C) predict the average number of occurrences of insurable events in a large population of policyholders. D) charge higher premiums than necessary, knowing that large numbers of individuals will pay them.
Federal antitrust laws in the United States are enforced
A) solely by the Federal Trade Commission. B) solely by the Department of Justice. C) by the Department of Justice and by the Federal Trade Commission. D) by the Department of Commerce.
Assume that the central bank increases the reserve requirement. If the nation has low mobility international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the quantity of real loanable funds per time period and the nominal value of the domestic currency in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises, and nominal value of the domestic currency falls. b. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period falls, and nominal value of the domestic currency rises. c. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises, and nominal value of the domestic currency remains the same. d. The quantity of real loanable funds per time period rises, and nominal value of the domestic currency rises. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.