Describe the cycle of life and death we observe in the spiral arms
What will be an ideal response?
As the spiral-density wave moves through the gas and dust clouds, it prompts the rapid formation of the massive blue stars we find in the associations, born from hot, pink emission nebulae. But these massive stars evolve very quickly, blowing up as supernovae when hardly out of the nursery; their supernova shock waves reshock the medium, leading to formation of many more less massive Population I stars like our own Sun farther behind the density wave.
You might also like to view...
Suppose you live at latitude 20°S. Based on the given right ascensions and declinations, which of the following stars passes closest to your zenith on its daily path through your sky?
A) Sirius: RA = 6hr 45m, dec = -16°42' B) Canopus: RA = 6hr 24m, dec = -52°41' C) Alpha Centauri: RA = 14hr 40m, dec = -60°50' D) Arcturus: RA = 14hr 16m, dec = +19°11' E) Vega: RA = 18hr 37m, dec = +38°47'
How are elements heavier than iron made? Why are they rare?
What will be an ideal response?
If Q = 20 ?C and L = 60 cm, what is the magnitude of the electrostatic force on any one of the charges shown?
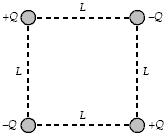
a.
25 N
b.
19 N
c.
15 N
d.
9.1 N
e.
14 N
Which of these statements correctly compares battery cells in series with the cells in parallel?
a. When battery cells are in series, the voltage stays the same but the cells last longer. b. When battery cells are in parallel, the voltage increases, but the cells last the same amount of time. c. When battery cells are in series, the voltage increases and the cells last longer. d. When battery cells are in parallel, the voltage stays the same and the cells last longer. e. When battery cells are in parallel the voltage is the same and they last just as long as when the cells are in series.