The equilibrium price and quantity of a good under perfect competition are determined:
A) by the intersection of the market demand and total revenue curves.
B) by the intersection of the total revenue and total cost curves.
C) by the intersection of the market demand and market supply curves.
D) by the intersection of the market supply and total revenue curves.
C
You might also like to view...
The figure above shows a labor market. If this labor market is perfectly competitive, the wage rate is
A) $4 per hour. B) $6 per hour. C) $8 per hour. D) $10 per hour.
If a monopolistically competitive firm breaks even, the firm
A) is earning zero accounting and zero economic profit. B) should expand production. C) is earning an accounting profit and will have to pay taxes on that profit. D) should advertise its product to stimulate demand.
Adjusted R2 gives the actual percentage of the variation in the dependent variable explained by the regression model
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the above figure. Which panel demonstrates the law of supply?
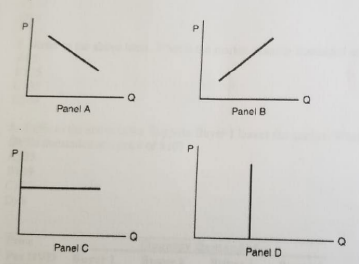
A) Panel A
B) Panel B
C) Panel C
D) Panel D