What is the magnetic force on a 2.0-m length of (straight) wire carrying a current of 30 A in a region where a uniform magnetic field has a magnitude of 55 mT and is directed at an angle of 20° away from the wire?
a. 1.5 N
b. 1.3 N
c. 1.1 N
d. 1.7 N
e. 3.1 N
c
You might also like to view...
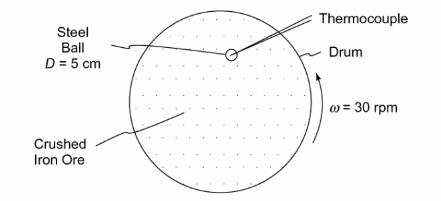
In the experimental determination of the heat transfer coefficient between a heated steel ball and crushed mineral solids, a series of 1.5% carbon steel balls were heated to a temperature of 700°C and the center temperature-time history of each was measured with a thermocouple as it cooled in a bed of crushed iron ore that was placed in a steel drum rotating horizontally at about 30 rpm. For a 5-cm-diameter ball, the time required for the temperature difference between the ball center and the surrounding ore to decrease from 500°C initially to 250°C was found to be 64, 67, and 72 s, respectively, in three different test runs. Determine the average heat transfer coefficient between the ball and the ore. Compare the results obtained by assuming the thermal conductivity to be infinite
with those obtained by taking the internal thermal resistance of the ball into account.
GIVEN
Heat steel balls are put in crushed iron ore
Balls are 1.5% carbon steel balls
Initial temperature of balls (To) = 700°C
Ball diameter = 5 cm = 0.05 m
Temperature difference between the ball center and the ore
Center temperature of the balls decreases from 500°C to 250°C
Time taken was found to be 64, 67, and 72 s, respectively, in three different test runs
FIND
The average heat transfer coefficient between the ball and the ore.
Compare the results obtained
(a) by assuming the thermal conductivity to be infinite with
(b) those obtained by taking the internal thermal resistance of the ball into account
ASSUMPTIONS
Temperature of the iron ore is uniform and constant
SKETCH
What are the differences between neap tides and ebb tides?
a -The tidal range of a spring tide is larger than the tidal range of a neap tide. b -During a spring tide, the moon, Earth and sun are aligned along a single line. During a neap tide, the moon and sun act on the Earth in right angles.\ c -When a spring tide occurs, the moon is new or full. When a neap tide occurs. The moon is at first quarter or new quarter. d -All of the above
A ball falls from the top of a building, through the air (air friction is present), to the ground below. How does the kinetic energy (K) just before striking the ground compare to the potential energy (U) at the top of the building?
A) K is equal to U. B) K is greater than U. C) K is less than U. D) It is impossible to tell.
The three principal sources of the internal heat of terrestrial planets are
A) accretion, differentiation, and eruption. B) accretion, differentiation, and radioactivity. C) convection, differentiation, and eruption. D) conduction, convection, and eruption. E) conduction, differentiation, and accretion.