Monopolists are like perfectly competitive firms in that ______.
a. both maximize profits at the output level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost
b. both could be earning either profits or losses in the short run
c. both are in industries with downward-sloping demand curves
d. all of these are true of both of them
e. both maximize profits at the output level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and both could be earning either profits or losses in the short run are true of both of them, but not both are in industries with downward-sloping demand curves
Ans: e. both maximize profits at the output level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and both could be earning either profits or losses in the short run are true of both of them, but not both are in industries with downward-sloping demand curves
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is not an advantage of cost-plus pricing?
A) If a firm is selling multiple products, it ensures that the firm's prices will cover costs that are difficult to assign to one product. B) It ensures that the firm will maximize its profits. C) It is easy to calculate. D) It requires little information.
In a perfectly competitive market, the demand curve faced by each firm is:
a. highly inelastic. b. perfectly elastic. c. perfectly inelastic. d. less elastic.
Suppose that each serving of Mac & Cheese costs $0.50 to make no matter how many servings are produced. This means that the price elasticity of supply for Mac & Cheese is ________ and the supply curve is ________.
A. infinite; perfectly elastic B. zero; perfectly elastic C. infinite; perfectly inelastic D. one; perfectly inelastic
Refer to the graph shown. If this monopolist produces 45 units of output per day, it will: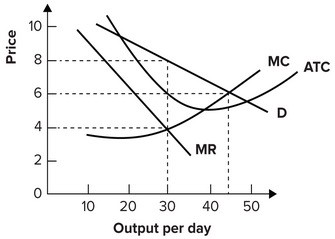
A. charge a price that exceeds its marginal cost. B. be maximizing profit. C. be able to increase profit by producing more per day. D. be able to increase profit by producing less per day.