Which of the following represents the basic principle of public choice theory?
A. Politicians act consistently in the public's interest.
B. Politicians follow their own self-interest and seek to maximize their reelection chances, rather than promote the best interests of society.
C. Politicians act in the public interest once they are elected, but follow their own self-interest and seek to maximize their reelection chances during a political campaign.
D. Politicians have an incentive to be cost-conscious and creative because they face the same type of profit motive as producers.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. Player B can infer that Player A will: 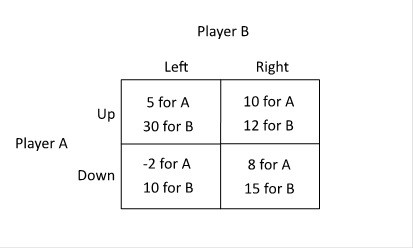
A. choose Down when B chooses Left and choose Up when B chooses Right. B. always choose Up. C. always choose Down. D. choose Up when B chooses Left and choose Down when B chooses Right.
Suppose the government increases the corporate income tax rate. This is
A) an expansionary fiscal policy that will shift the aggregate demand curve to the right by an amount equal to the initial change in corporate income tax revenue times the spending multiplier. B) a contractionary fiscal policy that will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left by an amount equal to the initial change in investment times the spending multiplier. C) a contractionary fiscal policy that will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left by an amount equal to the initial change in the corporate income tax rate times the spending multiplier. D) an automatic fiscal policy that will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left by an amount equal to the initial change in investment times the spending multiplier.
When demand falls, the price charged by a monopoly under an average-cost pricing policy will fall.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
The marginal benefit of another T-shirt this month to Mary is $15. If the $10 price of a T-shirt reflects its marginal cost to Mary and Mary uses economic reasoning, she:
A. will not buy a T-shirt this month. B. will not gain anything by buying another T-shirt. C. will sell the T-shirts she has to others who are willing to pay $10. D. will buy another T-shirt this month.