Explain how it is possible that there are moons within habitable zones that have habitable surfaces in other solar systems given that no such thing exists in our own solar system
What will be an ideal response?
They may form as a consequence of giant impacts like that which formed our own Moon. Also, planetary migration may allow for large jovian planets and their moons to migrate in to habitable zones.
You might also like to view...
____ are star-like objects that contain less than 0.08 solar masses an will never raise their core temperatures high enough that the proton-proton chain can begin. Other minor fusion reactions do occur in these objects. They fall in a gap between the low-mass M dwarf stars and the massive planets in which nuclear fusion never occurs
a. Brown dwarfs b. Herbig-Haro objects c. Bok globules d. T-Tauri star e. Main sequence stars
Which of the following results shows the validity of the relativistic effect of time dilation?
A) the detection of gravity waves B) bending of light near the Sun C) the decay of muons D) red shift in distant galaxies E) blue shift in distant galaxies
Determine the energy stored in the 40-?F capacitor
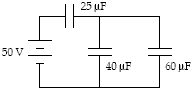
a.
2.4 mJ
b.
1.6 mJ
c.
2.0 mJ
d.
2.9 mJ
e.
4.0 mJ
Solenoid #1 has a length L, cross-sectional area A, and N turns. Solenoid #2 has a length 2L, cross-sectional area 2A, and 2N turns. Which long solenoid has the greater magnetic field at its center when equal currents are going through them?
a. Both have the same magnetic field. b. #1 c. #2 d. Since it depends on the values of A and L, none of the above are correct.