In Figure 4.2, the reason that the increase in output from point A to B is much less than the increase in output from point B to C is that 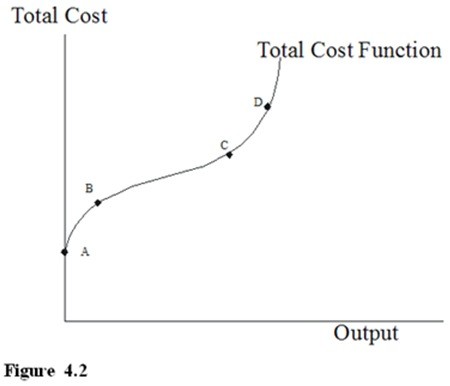
A. it is very difficult and very expensive to increase output once the capacity of the machinery has been reached.
B. it always costs more money to increase output.
C. small levels of production are often inefficient and that significant increases in production can occur thereafter at only a small additional cost.
D. there is waste.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Suppose exports and imports both rise by $1. GDP
A) rises by $2. B) rises by $1. C) remains unchanged. D) falls by $1. E) falls by $2.
The world price of a commodity will settle at the level where a. supply and demand are equal within each country
b. the excess demand of the importing country is just equal to the excess supply of the exporting country. c. the excess demand in the exporting country is equal to the excess demand in the importing country. d. there is no excess demand in the exporting country.
Households make their savings available to borrowers through
a. resource markets b. the loanable funds market c. the labor market d. the taxes e. spending
At his profit-maximizing level of output, a monopolist's average total cost curve is tangent to his demand curve. The monopolist
a. is earning a negative economic profit. b. may or may not be earning a negative economic profit. c. is earning zero economic profit. d. is earning a positive economic profit.