Compare the rate of heat loss from a human body with the typical energy intake from consumption of food (4.325 MJ/day). Model the body as a vertical cylinder 30 cm in diameter and 1.8-m-high in still air. Assume the skin temperature is 2°C below normal body temperature. Neglect radiation, transpiration cooling (sweating), and the effects of clothing.
GIVEN
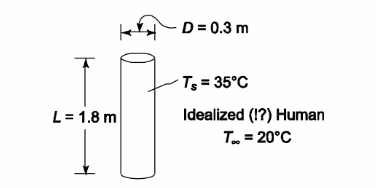
• Human body idealized as a vertical cylinder in still air
• Diameter (D) = 30 cm = 0.3 m
• Height (L) = 1.8 m
• Skin temperature (Ts) = 2°C below normal body temperature (37°C) = 35°C FIND
• Heat loss (q) and compare to consumption of food 4.325 MJ/day
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Radiation, transpiration cooling, and clothing effects are negligible
• Ambient air temperature (T?) = 20°C
• Heat loss from the top of the cylinder is small compared to that from the sides
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the mean temperature of 27.5°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00333 1/°C
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0257 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 16.4 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
The Grashof number based on the height is
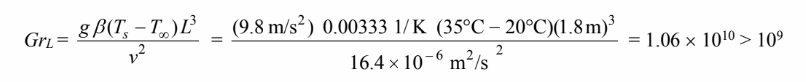
Therefore, the flow is turbulent.
For turbulent boundary layer, the average heat transfer coefficient is given by

The rate of convective heat loss from the sides of the cylinder is
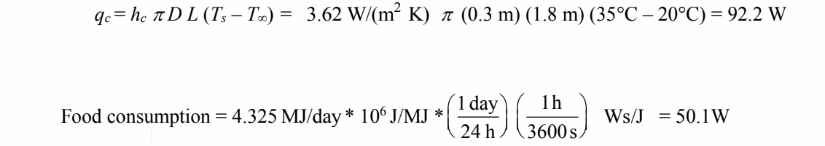
COMMENTS
The heat loss calculated for the idealized human is about 46% greater than the average food
consumption. This point out the importance of clothing.
You might also like to view...
If the diameter of a radar dish is doubled, what happens to its resolving power, assuming that all other factors remain unchanged?
A) The resolving power does not change unless the focal length changes. B) The resolving power is reduced to 1/4 of its original value. C) The resolving power is reduced to 1/2 of its original value. D) The resolving power doubles. E) The resolving power quadruples.
The following conversion equivalents are given: 1.0 mile = 5280 ft 1.0 ft = 12 in 1 m = 39.37 in 1.0 hour = 60 min 1.0 min = 60 s If a deer runs at 4.7 mi/h, its speed, in meters per second, is closest to
A) 2.1 m/s. B) 1.7 m/s. C) 1.9 m/s. D) 2.3 m/s. E) 2.5 m/s.
Which of the following is not one of the five major divisions of chemistry?
a. Nuclear chemistry b. Physical chemistry c. Biochemistry d. Inorganic chemistry
A 15-?F capacitor and a 25-?F capacitor are connected in parallel, and charged to a potential difference of 60 V. How much energy is then stored in this capacitor combination?
a. 50 mJ b. 18 mJ c. 32 mJ d. 72 mJ e. 45 mJ