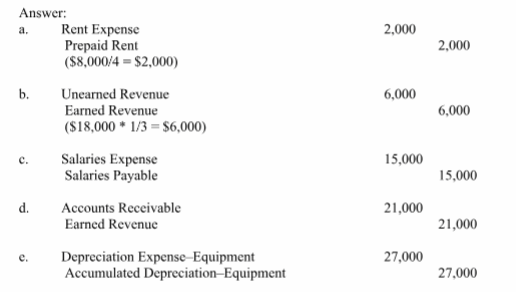
Prepare adjusting entries for the year ended December 31, for each of these separate situations. Assume that prepaid expenses are initially recorded in asset accounts and that fees collected in advance are initially recorded as liabilities.
a. The Prepaid Rent account has a debit balance of $8,000 before adjustment, representing a prepayment for four months' rent made on December 1 of the current year.
b. One-third of the work related to $18,000 of cash received in advance was performed during this period.
c. Unpaid accrued salaries at December 31 amounts to $15,000
d. Work was completed for a client on December 31 in the amount of $21,000, but was not previously billed or recorded.
e. Estimated depreciation on office equipment is $27,000.
You might also like to view...
The U.S. government will pay Turner Company $2,500,000 each six months, equal to 2.5% of the $100 million face amount of the treasury bonds (5% annual coupon rate, paid in two installments each year), and will repay the $100 million at the end of five years. At the time Turner Company purchases the bonds, the market prices these bonds to yield Turner Company 6% annually (3% each six months). The
bonds are classified as held to maturity. Because the market requires a _____ than the _____ on the bonds, the bonds will sell on the market for a _____ a. lower yield; stated interest rate; premium b. lower yield; market interest rate; premium c. higher yield; stated interest rate; discount d. lower yield; stated interest rate; discount e. market yield; stated interest rate; premium
The ____ part of my job is having the chance to work closely with the CEO
A) rewardingest B) most rewarding C) most rewardingest
A research report is informally structured. A research report is informally structured
Identify the correct equation for calculating the present value of an investment. (Assume 'r' stands for rate of return and 'n' stands for number of periods interest is earned.)
A. Present value = Future value × (1 + r)n B. Present value = Future value + (1 + r)n C. Present value = Future value - (1 + r)n D. Present value = Future value / (1 + r)n E. Present value = Future value / ((1 + r) × n)