Technology or production processes developed in a particular country:
A. may give that country a temporary comparative advantage.
B. may set that country back until they earn back the research and development costs.
C. will give that country a permanent comparative advantage.
D. generally are not transferrable to other nations.
A. may give that country a temporary comparative advantage.
You might also like to view...
Suppose paper pulp mills are permitted to emit harmful pollutants, free of charge, into the air. How will the price and output of paper in a competitive market compare with their values under conditions of ideal economic efficiency?
a. The price will be too high, and the output will be too large. b. The price will be too low, and the output will be too large. c. The price will be too low, and the output will be too small. d. The price will be too high, and the output will be too small.
Counting discouraged workers as unemployed would
A) lower the measured unemployment rate. B) raise the measured unemployment rate. C) raise the natural unemployment rate. D) raise the full employment rate. E) not change the measured unemployment rate.
An economy that operates inside its production possibility curve is less efficient than it would be if it were operating on its production possibility curve.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Refer to the information provided in Figure 15.2 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 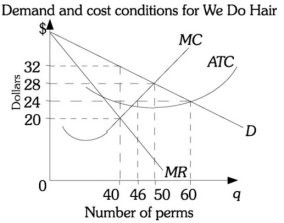 Figure 15.2 Refer to Figure 15.2. From society's point of view, the efficient level of output is
Figure 15.2 Refer to Figure 15.2. From society's point of view, the efficient level of output is
A. 40 perms. B. 50 perms. C. 60 perms. D. 80 perms.