The Keynesian cause-and-effect sequence predicts that a decrease in the money supply will cause interest rates to:
A. fall, boosting investment and shifting the AD curve rightward, leading to an increase in real GDP.
B. fall, boosting investment and shifting the AD curve rightward, leading to a decrease in real GDP.
C. rise, cutting investment and shifting the AD curve leftward, leading to a decrease in real GDP.
D. rise, boosting investment and shifting the AD curve rightward, leading to an increase in real GDP.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
According to the quantity theory of money, if the money supply grows at 6%, real GDP grows at 2%, and the velocity of money is constant, then the inflation rate will be
A) 8%. B) 6%. C) 4%. D) 2%.
Suppose the MPC is 0.9 . If autonomous consumption spending increases by $20 billion, equilibrium output will
a. increase by $22.2 billion b. increase by $200 billion c. not change because the MPC only changes consumption when income changes d. not change because the expenditures multiplier only applies to changes in investment spending and government purchases e. increase by $18 billion
Exhibit 4-6 Demand and supply curves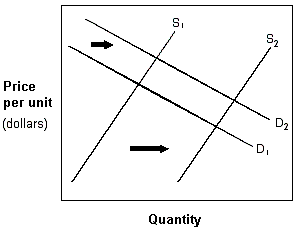
A. market price will decrease, and market quantity exchanged will increase. B. market price will increase, and market quantity exchanged will decrease. C. market price will increase, and the quantity exchanged could increase, decrease, or remain the same. D. market price could increase, decrease, or remain the same, and quantity exchanged will increase.
Generally speaking, the government implements fiscal policy in a:
A. fast but inaccurate manner. B. slow but accurate manner. C. slow and inaccurate manner. D. fast and accurate manner.