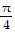Use mathematical induction to prove that the statement is true for every positive integer n.3 + 3 ? 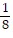 + 3 ?
+ 3 ? 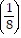 2 + ... + 3 ?
2 + ... + 3 ? 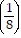 n - 1 =
n - 1 = 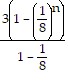
What will be an ideal response?
Answers will vary. One possible proof follows.
a). Let n = 1. Then, 3 = 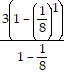 =
= 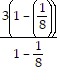 = 3. Thus, the statement is true for n = 1.
= 3. Thus, the statement is true for n = 1.
b). Assume that the statement is true for n = k:
Sk = 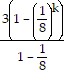
Also, if the statement is true for n = k + 1, then
Sk+1 = Sk + 3 ? 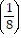 (k+1) - 1=
(k+1) - 1= 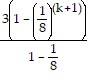
Substitute the expression for Sk into the one for Sk+1:
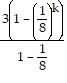 + 3 ?
+ 3 ? 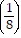 (k+1) - 1=
(k+1) - 1= 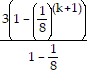
Collect the terms on the left-hand side over a common denominator:
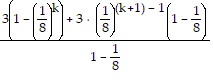 =
= 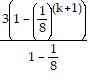
Expand the numerator of the left-hand side and simplify to get:
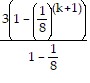 =
= 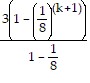
Since the equality holds, the statement is true for n = k + 1 as long as it is true for n = k. Furthermore, the statement is true for n = 1. Thus, the statement is true for all natural numbers n.
You might also like to view...
Round the following decimal to the indicated place. 3.14724; thousandths
A. 3.247 B. 3.048 C. 3.047 D. 3.147
Evaluate the integral.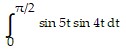
A. 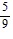
B. 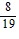
C. 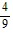
D. 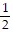
Find the first four terms of the binomial series for the given function.(1 + 6x)-1/2
A. 1 - 3x +  x2 -
x2 -  x3
x3
B. 1 - 3x +  x2 -
x2 - 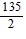 x3
x3
C. 1 - 3x - 27x2 -  x3
x3
D. 1 - 3x + 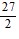 x2 -
x2 - 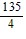 x3
x3
Show that the equation is not an identity by listing the value(s) of the variable from among 0, ?/4, ?/2, and - ?/4 for which the equation is false.sin ? + cos ? = tan ?
A. 0
B. 0 and 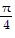
C. 0, 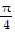 ,
, 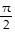 , and -
, and - 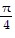
D. 0, 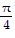 , and -
, and -