Suppose the Fed pursues a policy that leads to higher interest rates in the United States. How will this policy affect real GDP in the short run if the United States is an open economy? This policy
A) reduces investment spending and consumption spending, both of which reduce GDP. Net exports fall which increases GDP.
B) increases investment spending, consumption spending, and net exports, all of which increase GDP.
C) reduces investment spending and consumption spending, both of which reduce GDP. Net exports rise which increases GDP.
D) reduces investment spending, consumption spending and net exports, all of which reduce GDP.
D
You might also like to view...
The reserve ratio is 10 percent. If the bank receives a customer deposit of $100,000, then an immediate effect is
A) a reduction in the bank's total assets of exactly $10,000. B) no change in the bank's total assets or total liabilities. C) a reduction in the bank's total liabilities of exactly $10,000. D) an increase in the bank's reserves of exactly $10,000.
The above figure shows the Lorenz curve for wealth for the nation of Rusha. The poorest forty percent of the population own what percent of wealth?
A) 0 percent B) 10 percent C) 20 percent D) 40 percent
Suppose interest rates in the U.S. are 3% while interest rates on comparable bonds in Japan are 1%. By how much is the exchange rate between the yen and dollar expected to change according to the interest-rate parity condition?
What will be an ideal response?
There are 20 residents in the village of Towneburg. The size of the village's annual fireworks display depends upon the number of shells that are fired off. Each resident's demand for fireworks is shown below. The total cost of the fireworks display is $1,000 plus $10 per shell.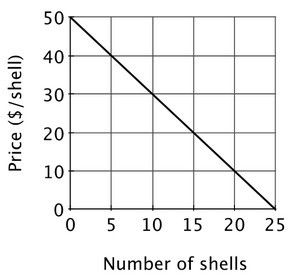 If Towneburg's fireworks display has 20 shells, then the size of the display is:
If Towneburg's fireworks display has 20 shells, then the size of the display is:
A. optimal. B. smaller than optimal. C. larger than optimal. D. unaffordable.