The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle serves all of the following functions EXCEPT?
A. It supplies key intermediates for the ultimate synthesis of amino acids, lipids, purines, and pyrimidines
B. It serves as the final common pathway for the complete oxidation of amino acids, fatty acids, and carbohydrates
C. It is the primary means in both bacteria and eukaryotic cells for the conversion of glucose to pyruvate
D. It is the major mechanism for the generation of ATP.
Ans: B. It serves as the final common pathway for the complete oxidation of amino acids, fatty acids, and carbohydrates
You might also like to view...
Osmoregulation is the control of ____
a. the internal environment b. temperature c. metabolic wastes d. water and ion balance e. hyperthermia
How many subunits make up a functional ribosome?
a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4
Investigate sexual selection by completing the sentences.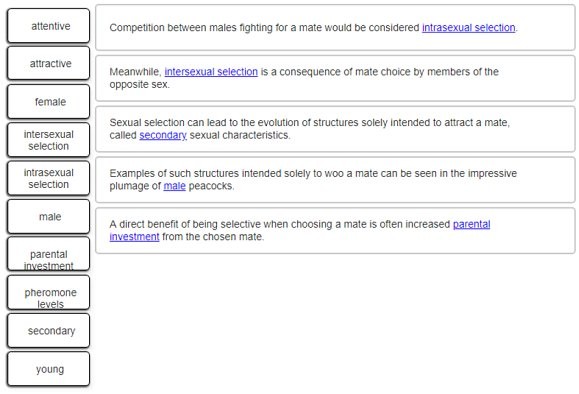
What will be an ideal response?
Identification of the type of stimulus causing the sensation occurs in the ____________
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).