Imagine Tom's annual salary as an assistant store manager is $30,000, he owns a building that rents for $10,000 yearly, and his financial assets generate $1,000 per year in interest. One day, after deciding to be his own boss, he quits his job, evicts his tenants, and uses his financial assets to establish a bicycle repair shop. To run the business, he outlays $15,000 in cash to cover all the costs involved with running the business, and earns revenues of $50,000. Tom should:
A. keep his shop going because he's earning a healthy $35,000 a year.
B. keep his shop going because he's earning $5,000 more than his salary before.
C. close his shop and go back to what he was doing before with his time and assets, because it was earning him $6,000 more than he's earning now.
D. None of these is true.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
In the above table, the production of 3 pizzas and 35 cases of soda is
A) impossible unless more resources become available. B) feasible but would involve unemployed or misallocated resources. C) possible only if the economy produces with maximum efficiency. D) possible only if there is inflation.
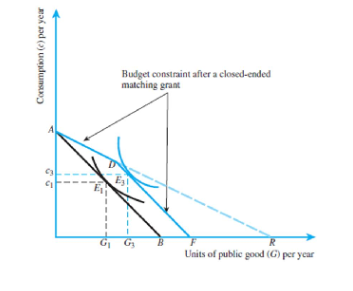
Refer to Figure 22.5 below. Suppose that the initial budget constraint AB is given by the equation G = 150 - c/5, where G is the units of public good and c is consumption. A closed- ended matching grant up to 100 units of public good is proposed. If the slope of line segment AD is -2, write the equation of the new budget constraint after a closed-ended matching grant.
A change in the price of a good has two effects on the quantity consumed. What are these effects?
A) the income effect and the substitution effect B) the consumption effect and expenditure effect C) the total utility effect and marginal utility effect D) the utility effect and the budget effect
If the demand for money is relatively stable,
A) the velocity of money will be constant. B) the velocity of money will grow at a steady and predictable rate. C) a fixed growth rate for the nominal money supply will lead to a stable growth rate of nominal GDP. D) B and C are both correct.