If demand increases while supply simultaneously decreases, then the equilibrium quantity
A) always increases.
B) always decreases.
C) can never change.
D) none of the above
D
You might also like to view...
What is the conclusion in the prisoners' dilemma?
A) Firms should not enter a legal duopoly. B) Two prisoners acting in their own best interest harm their joint interest. C) There is no Nash equilibrium available to the prisoners. D) Prisoners do not act interdependently. E) Duopolies almost always reach their best outcome.
If the government increases its spending or reduces its taxes in order to influence the level of economic activity, it is engaging in
a. regulatory policy b. antitrust policy c. monetary policy d. fiscal policy e. supply-management policy
Refer to the following table showing a monopolist's demand schedule: 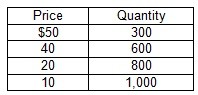 If price falls from $20 to $10, then
If price falls from $20 to $10, then
A. MR = -$30, and demand is inelastic. B. MR = -$10, and demand is inelastic. C. MR = $30, and demand is elastic. D. MR = $10, and demand is elastic. E. none of the above
The demand for good X is estimated to be Qxd = 10,000 ? 4PX + 5PY + 2M + AX where PX is the price of X, PY is the price of good Y, M is income, and AX is the amount of advertising on X. Suppose the present price of good X is $50, PY = $100, M = $25,000, and AX = 1,000 units. What is the demand curve for good X?
A. 61,500 B. 61,500 ? 4PX C. 61,300 ? 4PX D. 61,300