Use the following graph to answer the next question.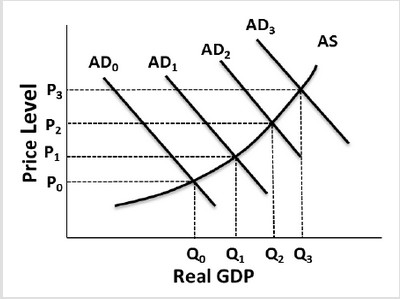 Suppose the economy is currently in equilibrium at the full-employment real GDP level of Q2.and price level of P2. If an event occurred in the economy that triggered demand-pull inflation, we would expect
Suppose the economy is currently in equilibrium at the full-employment real GDP level of Q2.and price level of P2. If an event occurred in the economy that triggered demand-pull inflation, we would expect
A. the price level to move toward P3, and the output level to move toward Q3,
B. the price level to move toward P3, and the output level to remain constant.
C. the price level to move toward P1, and the output level to move toward Q1,
D. the price level to move toward P1, and the output level to remain constant.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
How is foreign direct investment different from other types of international financial flows?
What will be an ideal response?
Clarence is a Japanese citizen working for Toyota at the manufacturing plant located in Tennessee. Clarence's work will contribute toward:
A. U.S. GDP since the location of the plant is in the U.S. B. Japan's GDP since he's a Japanese citizen. C. Japan's GDP since it's a Japanese firm. D. both the U.S. and Japan's GDP.
Assume that the government increases spending and finances the expenditures by borrowing in the domestic capital markets. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the real risk-free interest rate and current international transactions in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The real risk-free interest rate rises, and current international transactions become more positive (or less negative). b. The real risk-free interest rate falls, and current international transactions become more negative (or less positive). c. The real risk-free interest rate and current international transactions remain the same. d. The real risk-free interest rate rises, and current international transactions become more negative (or less positive). e. The real risk-free interest rate rises, and current international transactions remain the same.
Who guarantees that prices in the foreign exchange market are identical all over the world?
a. Governments. b. Supranational organizations. c. Central banks. d. Tourists. e. Arbitrageurs.