In a model with money neutrality, a 10% increase in the money supply leads to an increase of output by
A) more than 10%.
B) 10%.
C) less than 10%, but more than zero.
D) zero.
D
You might also like to view...
In perfect competition, each individual firm faces ________ demand curve
A) an inelastic B) an upward sloping C) a perfectly elastic D) a downward sloping
By looking at aggregate demand via its component parts, we can conclude that the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping because
A) a lower inflation rate causes the real interest rate to fall, and stimulates planned investment spending. B) a lower inflation rate causes the real interest rate to rise, and stimulates planned investment spending. C) a higher inflation rate causes the real interest rate to fall, and stimulates planned investment spending. D) a higher inflation rate causes the real interest rate to rise, and stimulates planned investment spending.
The reason that the Fed does not actively use discount rate policy to control the money supply is because the Fed
A. acts when a majority of member banks agree on policy and the banks rarely agree. B. earns interest on discounting and cannot afford to lose the revenue. C. does not know how banks will respond to discount rate changes. D. has been directed by Congress to set the discount rate at a permanent level.
If the tax cost of this proposed project is $600 per person, a majority vote will:
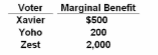
Answer the question on the basis of this table showing the marginal benefit a particular public project will provide to each of the three members of a community. No vote trading is allowed.
A. defeat this project and resources will be underallocated to it.
B. pass this project and resources will be allocated efficiently.
C. pass this project and resources will be overallocated to it.
D. pass this project and resources will be underallocated to it.