The demand curve for a monopolistically competitive firm is
A) more elastic than for a perfectly competitive firm.
B) more elastic than for a monopoly firm.
C) more inelastic than for a monopoly firm.
D) the same elasticity as a perfectly competitive firm.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The rationing function of price
A) occurs when there is a movement of resources into or out of markets as a result of changes in the equilibrium market price. B) is also known as the guiding function of price. C) occurs when consumers change their tastes and preferences. D) occurs only when the market experiences severe shortages.
If Ben values good X more than good Y and Catherine values good Y more than good X a firm can increase its profits by
A) charging the same price for both goods. B) bundling the goods. C) selling the goods in a competitive market. D) charging one price per good.
Multiplying the dependent variable by 100 and the explanatory variable by 100,000 leaves the
A) OLS estimate of the slope the same. B) OLS estimate of the intercept the same. C) regression R2 the same. D) variance of the OLS estimators the same.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD1 the result in the long run would be: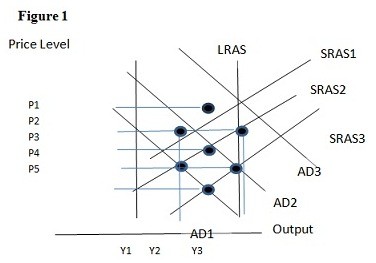
A. P4 and Y1. B. P4 and Y2. C. P5 and Y1. D. P5 and Y2.