What was the frost line of the solar system?
A) the distance from the Sun where temperatures were low enough for metals to condense, between the Sun and the present-day orbit of Mercury
B) the distance from the Sun where temperatures were low enough for rocks to condense, between the present-day orbits of Mercury and Venus
C) the distance from the Sun where temperatures were low enough for hydrogen compounds to condense into ices, between the present-day orbits of Mars and Jupiter
D) the distance from the Sun where temperatures were low enough for asteroids to form, between the present-day orbits of Venus and Earth
E) the distance from the Sun where temperatures were low enough for hydrogen and helium to condense, between the present-day orbits of Jupiter and Saturn
C
You might also like to view...
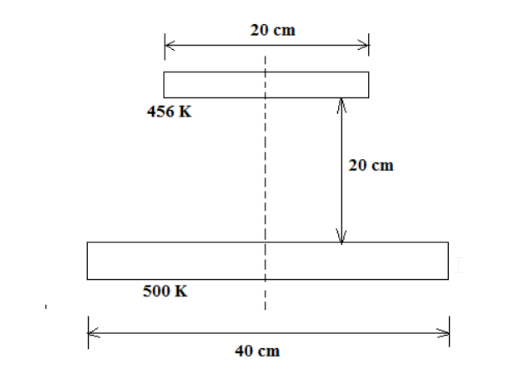
Two coaxial parallel plate discs are situated relative to each other as shown in the sketch. The diameter of the upper plate is 20 cm, and that of the lower plate is 40 cm. The lower plate is maintained at a uniform temperature of 500 K and the upper temperature is maintained at 456 K. To maintain these relative temperatures, a heater has to be installed in the upper plate. Assuming an environmental temperature of the surroundings at 300 K, determine the power necessary of the heater in the upper plate to maintain the two constant plate temperatures under steady state conditions.
GIVEN
• Two coaxial parallel plate discs at distance of L = 20 cm=0.2 m
• Upper plate diameter (D1) = 20 cm = 0.2 m
• Lower plate diameter (D2) = 40 cm = 0.4 m
• Upper plate temperature (T1) = 456 K
• Lower plate temperature (T2) = 500 K
• Surrounding temperature (Tsurr) = 300 K
FIND
(a) Power necessary of the heater in upper plate to maintain the constant plate temperatures under steady state conditions.
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
The Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
The disk of the galaxy is older than the halo
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The total mass of the Kuiper belt is greater than that of the asteroid belt
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Given that the above energy profiles have the same scale, which of the reactions would require the most energy?
A) a B) b C) c D) d E) none of the above