Radiation pressure: A radiometer has two square vanes (1.0 cm by 1.0 cm), attached to a light horizontal cross arm, and pivoted about a vertical axis through the center, as shown in the figure. The center of each vane is 6.0 cm from the axis. One vane is silvered and it reflects all radiant energy incident upon it. The other vane is blackened and it absorbs all incident radiant energy. Radiant energy, having an intensity of 300 W/m2, is incident normally upon the front of both vanes. What is the net torque on the vane assembly, about the vertical axis? (c = 3.0 × 108 m/s, ?0 = 4? × 10-7 T ? m/A, ?0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ? m2) 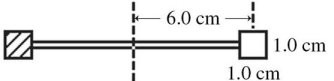
A. 0.0 N ? m
B. 6.0 × 10-12 N ? m
C. 1.2 × 10-11 N ? m
D. 1.8 × 10-11 N ? m
E. 2.4 × 10-11 N ? m
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The term "relativistic" refers to effects that are
A. measured by stationary observers only. B. observed when speeds are near the speed of light. C. observed when objects move backward in time. D. noticed about a moving object.
Light of wavelength 425.0 nm in air falls at normal incidence on an oil film that is 850.0 nm thick. The oil is floating on a water layer 15 cm thick
The refractive index of water is 1.33, and that of the oil is 1.40. You want to add oil so that light reflected off of the top of the oil film will be canceled. What is the minimum distance that you should INCREASE the oil film? A) 121 nm B) 152 nm C) 75.9 nm D) 106 nm E) 60.7 nm
Within the boundaries of the constellations Coma and Virgo are found
A) the largest nearby superclusters of galaxies. B) the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. C) the most distant known quasars. D) the closest red dwarfs to the Sun. E) all the galaxies in the Local Group.
An object consists of a rod (of length 3.00 m and negligible moment of inertia) to which four small 3.50-kg masses are attached, one at each end and one at each point on the rod spaced at 1.00-m intervals. The moment of inertia of this object about an axis perpendicular to the rod and through one of the end masses:
a. is 49 kg·m2. b. is 21 kg·m2. c. is 31.5 kg·m2. d. is 10.5 kg·m2. e. cannot be uniquely determined until it is stated which inner mass the axis goes through.