One of the most common examples of recursion is an algorithm to calculate the factorial of an integer. The notation n! is used for the factorial of the integer n and is defined as follows:
0! is equal to 1
1! is equal to 1
2! is equal to 2 _ 1 = 2
3! is equal to 3 _ 2 _ 1 = 6
4! is equal to 4 _ 3 _ 2 _ 1 = 24
. . .
n! is equal to n _ (n ? 1) _ (n ? 2) _ ... _ 3 _ 2 _ 1
An alternative way to describe the calculation of n! is the recursive formula
n * (n ? 1)!, plus a base case of 0!, which is 1. Write a static method that implements this recursive formula for factorials. Place the method in a test program that allows the user to enter values for n until signaling an end to execution.
This problem is very easy to write as a recursive algorithm. The base case returns one for n = 0 or n = 1. All other cases multiply the number passed by the return value of a recursive call for the passed number minus one. Note that the program loops until the user enters a non-negative number. One word of caution: it is easy to enter a number that will result in a calculated value too large to store. An interesting little project would be to have the students find out what the largest integer value is for the platform they are using, then determine which values to enter to bracket the maximum value, and run the program to see what happens when the those values are entered.
See the code in Factorial.java.
You might also like to view...
Use the output stream to the file autos.txt created above in number 2 to write the line “Mercedes” to the file.
What will be an ideal response?
Contents include underlying formulas and data
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
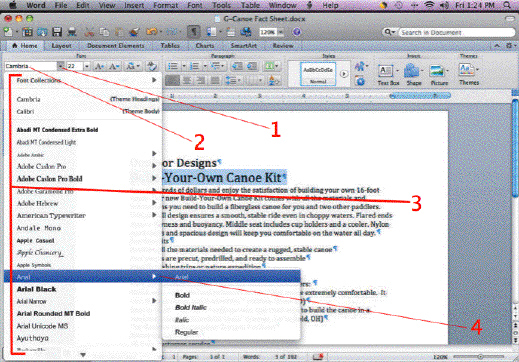 In the accompanying figure, Item 1 points to the ____.
In the accompanying figure, Item 1 points to the ____.
A. Font Size pop-up menu arrow B. Font Color pop-up menu arrow C. Font pop-up menu arrow D. Font group pop-up menu arrow
Which of the following summarizes the logic followed by routers using ACLs in determining if a match occurs?
A) The router will search sequentially until it finds a match and stop. B) The router will search sequentially until it reaches the end of its list whether a match is found or not. C) The router will search its list to find all matches. D) The router will search its deny entries first and then search for its permit entries.