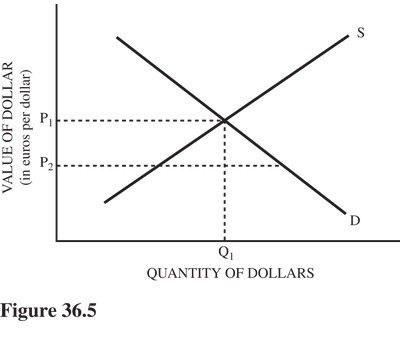
 Refer to Figure 36.5 for the dollar-euro foreign exchange market with the market exchange rate at P1. The European Union (EU) and U.S. governments have agreed on a fixed exchange rate of P2. This situation
Refer to Figure 36.5 for the dollar-euro foreign exchange market with the market exchange rate at P1. The European Union (EU) and U.S. governments have agreed on a fixed exchange rate of P2. This situation
A. Causes an excess demand for euros.
B. Requires that the EU buy U.S. dollars.
C. Causes a balance-of-payments deficit for the EU.
D. Calls for an expansionary fiscal policy in the EU.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Using the definition of unemployment, which of the following individuals would be unemployed?
A) A full-time student quits school, enters the labor market for the first time, and searches for employment. B) Because of the increased level of automobile imports, an employee of General Motors is laid off but expects to be called back to work soon. C) Because of a reduction in the military budget, your next door neighbor loses her job in a plant where nuclear warheads are made and must look for a new job. D) All of these individuals are unemployed.
If price is less than its minimum average variable cost, a perfectly competitive firm that continues to produce in the short run
a. cannot cover any of its variable cost b. incurs a loss greater than its fixed cost c. can cover all of its fixed cost and some of its variable cost d. can cover all of its variable cost and some of its fixed cost e. can cover both its fixed costs and its variable cost
If taxpayers can enjoy mosquito abatement whether or not they pay for it and, therefore, they tend to understate their true valuation of the spraying, this is an example of
a. private goods b. the median-voter model c. an open-access good d. the free-rider problem e. irrational ignorance
When is the U.S. economy at full employment?
a. When there is no cyclical unemployment b. When there is no structural unemployment c. When there is no full employment d. When there is no seasonal unemployment e. When there is no frictional unemployment