When (if at all) can the crowding-out effect be prevented?
A) when the Fed decreases the money supply to accommodate the expansionary fiscal policy
B) when the real money supply is held constant
C) when the real balance effect is working
D) when the Fed allows the real money supply to increase sufficiently to keep the interest rate from rising
D
You might also like to view...
A $100 annuity is
a. $100 received in a single year b. $100 received each year forever c. more or less than $100, dependent on the interest rate, received for a certain number of years d. $100 received each year for a certain number of years e. more or less than $100, dependent on the interest rate, received until an upper limit is reached
Suppose the velocity of money is 6, the amount of money in circulation is $600 billion, the index of prices is 180, and real GDP is $20 billion. According to the strict quantity theory of money, if the money supply decreased to $300 billion,
a. the velocity of money would rise to 12. b. the index of prices would fall to 90. c. real GDP would decrease to $10 billion. d. the velocity of money would decline to 3.
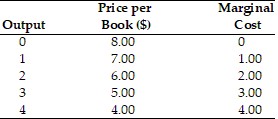 The above table depicts prices, quantities, and marginal costs faced by the campus bookstore. Based on marginal analysis, what is the profit-maximizing level of output for the bookstore?
The above table depicts prices, quantities, and marginal costs faced by the campus bookstore. Based on marginal analysis, what is the profit-maximizing level of output for the bookstore?
A. 1 book B. 2 books C. 3 books D. 4 books
In an effort to avoid recession, the government implements a tax rebate program, effectively cutting taxes for households. We would expect this to:
A. affect neither aggregate supply nor aggregate demand. B. increase aggregate demand. C. reduce aggregate demand. D. reduce aggregate supply.