Explain why Earth experiences different seasons throughout the year. Which parts of Earth experience the greatest seasonal variability, and which parts experience the least? Explain why
What will be an ideal response?
Seasonality is caused by the tilt, or obliquity, of the Earth. The hemisphere that faces the Sun receives much more solar energy than does the other hemisphere. It is this factor that determines the seasons. For six months of each year, the Northern part of the Northern Hemisphere leans towards the Sun and the Southern part of the Southern Hemisphere leans away, leading to Summer in the Northern Hemisphere and Winter in the Southern Hemisphere. For the other six months of the year, the opposite is true. The tropics are not greatly affected by this, because the tilt of the Earth is not extreme enough to significantly reduce incoming solar radiation near the equator. There is also a difference between land and ocean. Land surfaces at all latitudes tend to experience greater seasonal variation than do ocean surfaces. Continental interiors at high latitudes, therefore, have the greatest seasonality.
You might also like to view...
Explain this statement: The world's population growth has slowed, but the world's population is still growing. Include a comment about where the slowing has occurred
What will be an ideal response?
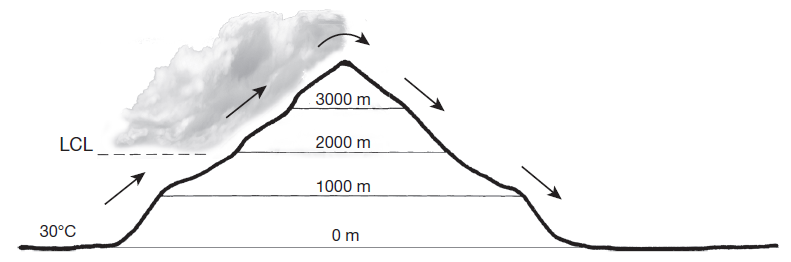
On the lee side of the mountain, is the relative humidity of the parcel increasing or decreasing as it descends from 4000 meters to sea level? Why?
Assume that a parcel of air is forced to rise up and over a 4000-meter-high mountain (as shown). The initial temperature of the parcel at sea level is 30°C, and the lifting condensation level (LCL) of the parcel is 2000 meters. The DAR is 10°C/1000 m and the SAR is 6°C/1000 m. Assume that condensation begins at 100% relative humidity and that no evaporation takes place as the parcel descends.
When there is an equilibrium between water in the air and water in the ocean, the air is said to be ____________________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
The growth of a precipitation particle by the collision of an ice crystal (or snowflake) with a supercooled liquid droplet is called?
a. ?accretion. b. ?spontaneous nucleation. c. ?condensation. d. ?deposition. e. ?collision.