What did the researcher do to cause the change in the shaded regions in the two distributions?
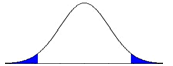
“Before”
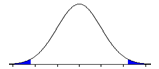
“After”
a. She changed alpha from .05 to .01.
b. She changed alpha from .05 to .10.
c. She changed from a directional to a non-directional alternative hypothesis.
d. She changed from a non-directional to a directional alternative hypothesis.
a. She changed alpha from .05 to .01.
You might also like to view...
How difficult should food activities be for children?
What will be an ideal response?
To find out if visual imagery (i.e., "picturing" things in one's mind) is more effective than verbal repetition in learning French vocabulary words, a French teacher develops two different study guides for her students: one that tells students how to use visual imagery to learn French words, and one that tells them to just repeat the words over and over. She randomly distributes the two study
guides to her students. Over the next few weeks, the teacher finds that students using visual imagery study guides achieve higher average quiz scores. Because all of the students used their given study guides and there was no reason to suspect other differences between the two groups of students, she concludes that the visual imagery study guide helped her students to learn their French vocabulary words more than the other study guide. Is the teacher's conclusion valid for her students? A) No, because she used random assignment B) No, because her experiment wasn't conducted in a laboratory C) Yes, because her students probably all had similar IQ scores D) Yes, because she was able to manipulate a variable in the environment
Most children have mastered the sounds of English by
a. age 4 b. age 8 c. age 5 d. age 10
Discuss the prerequisite for differentiating instruction regarding the students.
What will be an ideal response?