Elastic Collisions: A block of mass m = 3.6 kg, moving on a frictionless surface with a speed vi = 9.3 m/s, makes a sudden perfectly elastic collision with a stationary block of mass M, as shown in the figure. Just after the collision, the 3.6-kg block recoils with a speed of vf = 2.7 m/s. What is the speed V of the other block?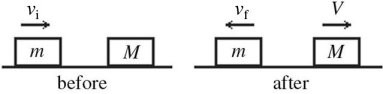
A. 6.6 m/s
B. 8.0 m/s
C. 9.3 m/s
D. 10.7 m/s
E. 12.0 m/s
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Predict the concentration of ammonia in air 5 mm from an interface of vapor ammonia and air if the interface area is 1500 mm^2 and the evaporation rate is found to be 0.002 g/min. Assume the ammonia and air are at 20ºC.
What will be an ideal response?
Two wires have a nearly equal electron number density. Assume that the electric field in each wire points directly along the wire, that electric fields in the two wires have the same magnitude, but that the conductivity in wire A is twice that in wire B. This means that the drift velocity in wire A is b times that in wire B, where b is
A. 4 B. 2 C. 1 D. 1/2 E. 1/4 F. Impossible to determine from the given information
Recent evidence suggests that Mars once had a global magnetic field. Assuming this is true, which of the following could explain why Mars today lacks a global magnetic field like that of Earth?
A) Mars rotates much slower than the Earth. B) The Martian core is made of rock, while Earth's core is made of metal. C) Mars's interior has cooled so much its molten core layer no longer undergoes convection. D) Mars is too far from the Sun to have a global magnetic field.
If the length of a wire increases, its resistance decreases
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false