Velocity Addition: Two spaceships, each 100 m long in its own rest frame, approach Earth from opposite directions, each with a speed 0.50c relative to Earth. As measured by a passenger in one of the spaceships, how long is the other spaceship?
A. 50 m
B. 60 m
C. 70 m
D. 80 m
E. 90 m
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
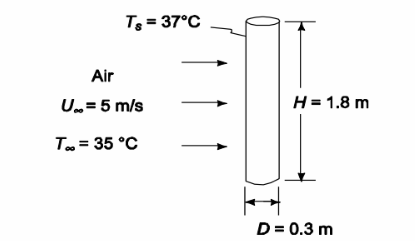
The human body is typically modelled as a vertical cylinder that is 1.8 m high and is 30 cm in diameter, as shown in the figure. Calculate the average rate of heat loss from this body, which is maintained at 37°C, on a windy day when the airstream has a 5 m/s velocity and is at 35°C. To ascertain “wind chill” effects, compare this result with the heat loss that would occur in “stagnant” conditions, or when it is not windy and the heat transfer is only by natural convection (consider an average heat transfer coefficient of 3.6 W/(m2 K) for free convection). What is the wind chill effect if the wind got stronger (10 m/s) and colder (25°C)? Even though the natural convection heat transfer coefficient also changes somewhat (as discussed later in Chapter 8), for this calculation
consider it to remain the same. Moreover, compare the heat loss in both cases with the typical energy intake, or metabolic heat production from consumption of food, of about 1033 kcal/day and comment upon your results.
GIVEN
• Human body modeled as a cylinder in an air stream
• Body surface temperature (Ts) = 37°C
• Air velocity (V?) = 5 m/s
• Air temperature (T?) = 35°C
• Cylinder diameter (D) = 30 cm = 0.3 m
• Cylinder height (H) = 1.8 m
FIND (a) The heat loss from the idealized human body
(b) Heat loss if the wind speed is 10 m/s and its temperature is 250C. (c) Compare with the free convection results of Problem 5.8 and with the typical food
consumption rate of 1033 kcal/day
ASSUMPTIONS
• Air velocity is perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder
• Air flow approaching cylinder is laminar
• Heat transfer from the ends can be neglected
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0262 W/(m K) Kinematic viscosity (?) = 17.1 × 10–6 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 At the surface temperature of 37°C Prs = 0.71
An n-type semiconductor is produced in polyacetylene by doping with:
(a) Arsenic (b) Phosphorus (c) Fluorine (d) Lithium
A parallel plate capacitor has a paper dielectric having dielectric strength 8.0 kV/mm and dielectric constant 3.0. The plate area is 3000 cm2 and the plate separation is 0.50 mm. What is the capacitance?
A. 16 nC B. 4.2 nC C. 5.3 nC D. 1.6 nC E. 4.2 pdf
Energy flows by radiation or convection inside stars but almost never by conduction
Indicate whether the statement is true or false