Artificially scarce goods are both:
a. excludable and rival in consumption.
b. nonexcludable and nonrival in consumption.
c. excludable and nonrival in consumption.
d. nonexcludable and rival in consumption.
Ans: c. excludable and nonrival in consumption.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements is true?
(a) larger countries (in terms of size) tend to be more open (in terms of larger share of exports in GDP) than smaller countries and developing countries tend to be less open than developed economies. (b) larger countries (in terms of size) tend to be less open (in terms of lower share of exports in GDP) than smaller countries and developing countries tend to be less open than developed economies. (c) larger countries (in terms of size) tend to be more open (in terms of larger share of exports in GDP) than smaller countries and developing countries tend to be more open than developed economies. (d) larger countries (in terms of size) tend to be less open (in terms of lower share of exports in GDP) than smaller countries and developing countries tend to be more open than developed economies.
Which of the following is a basic assumption of the Ricardian equivalence theorem?
A) Consumers pay no attention to government budget deficits. B) Consumers think only in terms of the present. C) If current tax cuts result in budget deficit increases, aggregate supply falls. D) Consumers consider future tax payments when deciding how much to spend and save today.
When the price of wheat increases, the producers of bread will supply more bread at each price
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the table at right. If the price is? $6, the perfectly competitive firm should produce
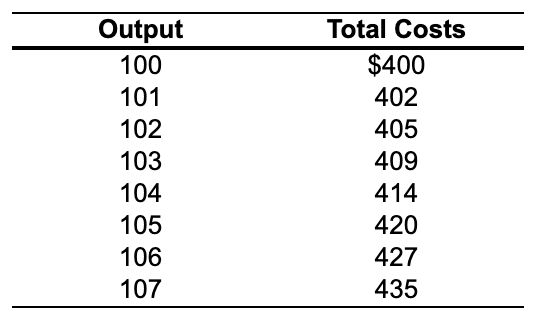
A. 107 units
B. 104 units
C. 106 units
D. 105 units