In the long run, fixed costs are
A) sunk.
B) avoidable.
C) larger than in the short run.
D) not included in production decisions.
B
You might also like to view...
The Bubby Gum factory produces bubble gum. Joanne is one of the employees, and she produces 10 packs of bubble gum per hour. Joanne's money wage rate is $12 per hour. If a packet of bubble gum sells for $1.00, then
A) Joanne is creating a $2.00 per hour profit for the firm. B) Joanne is creating a $2.00 per hour loss for the firm. C) the Bubby Gum company should pay Joanne more. D) the Bubby Gum company should decrease the price of the bubble gum so it sells more and makes a larger profit. E) None of the above answers is correct because more information about Joanne's real wage is needed to decide what to do.
If a country's currency has a market driven value that is higher than economic theory would suggest, the currency is considered to be
A) overvalued. B) undervalued. C) overestimated. D) in arbitrage.
A positive externality exists when
A. a person's or group's actions cause a benefit that is felt by others. B. a person's or group's actions cause a cost that is felt by others. C. market output is less than socially optimal output. D. a and c E. b and c
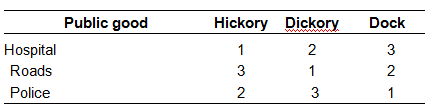
Explain the paradox of voting that is illustrated in the table below in choices between the same expenditure on three different public goods. The numbers under each name indicate the voting preferences (first, second, or third choice) of each of the
three citizens in the society.