The original comparative advantage model that used the relative abundance of factors of production to explain comparative advantage assumed that countries:
a. employed all four factors of production; land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
b. employed only two factors of production; labor and capital.
c. employed only two factors of production; land and entrepreneurial ability.
d. worked with a fixed capital stock.
e. were free to vary their employment of only one factor of production; labor.
b
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. An industry's demand curve tends to be more elastic than the sum of the individual firms' labor curves. 2. A monopsonist's short-run demand curve for labor coincides with its marginal revenue product of labor curve. 3. A monopsonist will continue to hire additional laborers as long as their marginal revenue product exceeds the wage rate. 4. A monopsonist hires fewer workers and pays a lower wage than would be the case if many firms competed to hire labor. 5. The profit an owner receives is equivalent to the rent received for her entrepreneurial services.
An adverse supply shock shifts the short-run Phillips curve right and the short-run aggregate-supply curve left
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The term "open market operations" refers to the:
A. loan-making activities of commercial banks. B. effect of expansionary monetary policy on interest rates. C. operation of competitive markets in the banking industry as the result of deregulation. D. buying and selling of government securities by the Federal Reserve.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD3 to AD2 the result in the short run would be: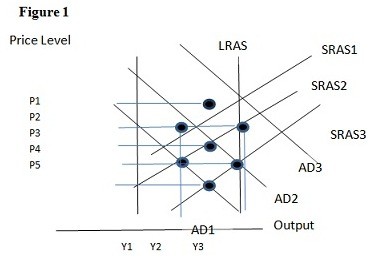
A. P3 and Y1. B. P2 and Y1. C. P2 and Y3. D. P1 and Y2.