In classical IS—LM analysis, the effects of a decline in desired investment include
A) a decline in output.
B) an increase in the price level.
C) a decline in the real interest rate.
D) an increase in unemployment.
C
You might also like to view...
What is a primary market?
A) a market where primary inputs like steel are sold B) a market where you can sell any stocks you own as a private investor C) a market where you can sell any bonds you own as a private investor D) a market where newly issued claims are sold to initial buyers by the borrowing firm
Suppose a perfectly competitive increasing-cost industry is in long-run equilibrium when market demand suddenly increases. What happens to the typical firm in the long run?
a. It experiences no change from the original equilibrium b. It experiences a higher average total cost and equilibrium price c. It experiences a lower average total cost and equilibrium price d. It experiences the same equilibrium price but a greater average total cost e. It experiences the same equilibrium price but a lower average total cost
Exhibit 5-1 Demand curve
?
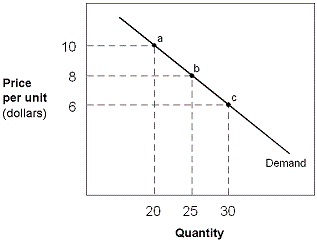
A. buy twice as much of the product in response to a 10 percent decrease in prie. B. require a 2 percent drop in price to increase their purchases by 1 percent. C. buy 2 percent more of the product in response to a 1 percent decrease in price. D. buy twice as much of the product in response to a 1 percent decrease in price.
Effectively removing all illegal immigrants from U.S. labor markets would:
A. reduce wages in the United States. B. increase employment of domestic-born workers, but by a lesser amount than the number of jobs lost by illegal workers. C. increase employment of domestic-born workers at a rate of one-for-one with the jobs lost by illegal workers. D. increase employment of domestic-born workers by an amount greater than the number of jobs lost by illegal workers.