This graph shows three different budget constraints: A, B, and C.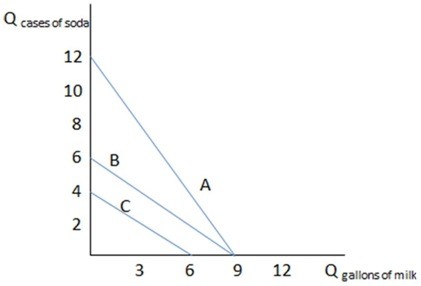 If Daniel has budget constraint C in the graph shown, what would cause it to shift to budget constraint B?
If Daniel has budget constraint C in the graph shown, what would cause it to shift to budget constraint B?
A. A decrease in the price of soda
B. An increase in the price of soda
C. An increase in the price of milk
D. None of these changes alone could cause a shift from C to B.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
If the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, eventually the
A) AS curve shifts rightward, decreasing real GDP and raising the price level. B) AS curve shifts leftward, decreasing real GDP and raising the price level. C) AD curve shifts leftward, decreasing real GDP and raising the price level. D) AD curve shifts leftward, decreasing real GDP and lowering the price level. E) AD curve shifts rightward, increasing real GDP and raising the price level.
An expansion ends when the economy hits a trough and then enters a recession
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Despite the fact that gross savings in the U.S. has been declining, we have been able to invest billions of dollars to purchase additional plant and equipment because
A. the federal government balanced the budget. B. foreign savers made up the difference. C. the government ran a budget surplus. D. personal savings was over 10 percent.
A firm that must determine the price-output combination that maximizes profit because it faces a downward-sloped demand curve
A) has a perfectly elastic demand curve. B) has a perfectly inelastic demand curve. C) is a price-taker. D) is a price searcher.