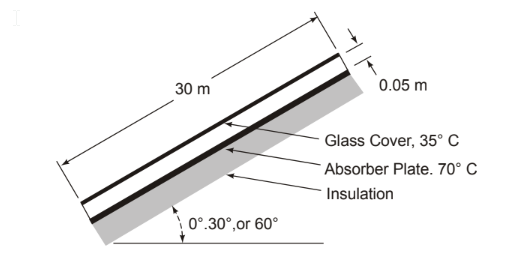
A flat plate solar collector of 3 m ? 5 m area has an absorber plate that is to operate at a temperature of 70°C. To reduce heat losses, a glass cover is placed 0.05 m from the absorber. Its operating temperature is estimated to be 35°C. Determine the rate of heat loss from the absorber if the 3 m edge is tilted at angles of inclination from the horizontal of 0°, 30°, and 60°.
GIVEN
• A flat plate solar collector
• Area = 3 m × 5 m
• Absorber temperature (Ta) = 70°C
• Glass cover temperature (Tc) = 30°C
• Distance between absorber and cover (?) = 0.05 m
FIND
Heat loss by natural convection from the absorber of angles (?) of (a) 0°, (b) 30°, and (c) 60° from the horizontal
ASSUMPTIONS
• The space is air filled
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the mean temperature of 52.5°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00307 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0274 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 18.7 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
The Grashof and Rayleigh numbers for this geometry are
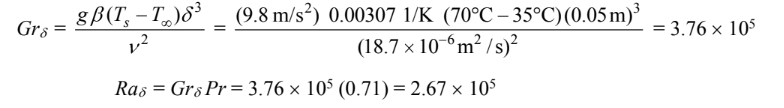
The heat transfer coefficient is given by Equation (8.31), where the quantities enclosed by [ ] are to be set to zero if they are negative: At ? = 0°. Since the aspect ratio (L/?) = 3/0.05 = 60, the critical angle is 70°
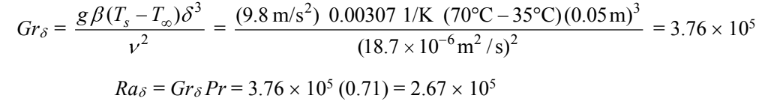
The rate of natural convective heat transfer is given by
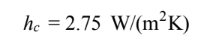
Performing a similar calculation for the other angles yields the following results
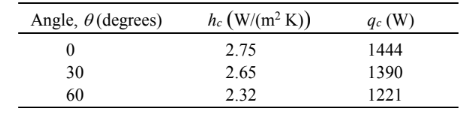
COMMENTS
Heat transfer by radiation will also be significant in this case.
You might also like to view...
In discussing the electron double-slit experiment, we studied a graph of the extended wave pattern formed on the screen by each electron's matter field
Did this graph show a single electron's matter field just before, or just after, the electron strikes the screen, and why? A) This is the matter field just after impact, because each electron actually spreads out over a large region and strikes all over this region, in a wave pattern. B) This is the matter field just before impact; after impact, the electron acquires a definite velocity. C) This is the matter field just before impact; after impact the matter field transforms into two distinct parts, with one part appearing on the screen directly behind each slit. D) This is the matter field just after impact, because the electron can strike the screen at a wide variety of specific places, and these places form a field pattern. E) This is the matter field just before impact; after impact the matter field collapses into a small region around the impact.
Which of the following best describes a substance in which the temperature remains constant while at the same time it is experiencing an inward heat flow?
a. gas b. liquid c. solid d. substance undergoing a change of state
A 0.150-m-radius grinding wheel, starting at rest, develops an angular speed of 12.0 rad/s in a time interval of 4.00 s. What is the centripetal acceleration of a point 0.100 m from the center when the wheel is moving at an angular speed of 12.0 rad/s?
a. 0.450 m/s2 b. 7.20 m/s2 c. 14.4 m/s2 d. 28.8 m/s2
One ray that is useful in locating the image formed by a convex mirror is the ray that is incident on the mirror in a path directed toward the focal point. This ray is reflected
A. through the center of curvature. B. directly back along its incident path. C. on a path tangent to the mirror. D. on a path parallel to the mirror axis.