Only during the last decade of the twentieth century did the Arctic began to experience an ozone hole and formation of polar stratospheric clouds, and the hole expanded in a regular way after it appeared
What does this indicate about Arctic stratospheric temperatures during this period? Explain.
As a result of detailed study of the mechanisms of ozone depletion, we know that
the temperature has a lot to do with what happens. The temperature near the poles is very
low. That is really all that we can know based on this particular observation. We can know
that because we know that low temperatures are essential for the ozone-depleting reactions
to occur. But other conditions must be met as well.
Does the expanded ozone hole mean that the temperature must have gotten lower? Not
necessarily. The concentration of ozone-depleting gases may have changed.
Is the temperature on this basis then known not to be lower than in previous times? This is
not knowable on the basis of this observation alone; it may or may not have happened (see
the preceding paragraph).
Can we be sure the concentration of ozone-depleting gases has changed? Certainly not on
the basis of this observation alone; the temperature or some other condition could have
changed. This is the reason that we can conclude only that the temperature must have been
low enough for the requisite chemical reactions to occur.
You might also like to view...
Instructions: On occasion, the notation 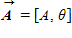
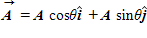
When vector 
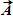
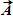
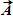
A girl throws a stone from a bridge. Consider the following ways she might throw the stone. The speed of the stone as it leaves her hand is the same in each case, and air resistance is negligible. Case A: Thrown straight up
Case B: Thrown straight down. Case C: Thrown out at an angle of 45° above horizontal. Case D: Thrown straight out horizontally. In which case will the speed of the stone be greatest when it hits the water below? A) Case A B) Case B C) Case C D) Case D E) The speed will be the same in all cases.
Doubling the wavelength of a photon would ______________ its energy
a. halve b. double c. quadruple d. not change
The flux through a coil changes from 4.0 × 10-5 Wb to 5.0 × 10-5 Wb in 0.10 s. What emf is induced in this coil?
A) 5.0 × 10-4 V B) 4.0 × 10-4 V C) 1.0 × 10-4 V D) 0 V E) none of the given answers