The route followed by a sperm from production to fertilization in a flowering plant is:
A. A sperm cell, enclosed in a pollen grain with another sperm, is produced in the pistil that explosively ejects it into the air where it is transported to a stigma from which it passes through a pollen tube that grows down the style to the ovary, enters the ovule and joins with the egg cell.
B. A sperm cell, enclosed in a pollen grain with another sperm, is produced in the anther, transported to a stigma where it passes through a pollen tube that grows down the style to the ovary, enters the ovule and joins with the egg cell.
C. A sperm cell, enclosed in a pollen grain with another sperm, is produced in the filament, transported to a stigma where it passes through a pollen tube that grows down the style to the ovary, enters the ovule and joins with the egg cell.
D. A sperm cell, enclosed in a pollen grain with another sperm, is produced in the anther, transported to the peduncle where it passes through a pollen tube that grows down the style to the ovary, enters the ovule and joins with the egg cell.
E. A sperm cell is produced in the anther, transported to a stigma where it becomes enclosed, along with another sperm cell into a pollen grain that grows down the style to the ovary, enters the ovule and joins with the egg cell.
B. A sperm cell, enclosed in a pollen grain with another sperm, is produced in the anther, transported to a stigma where it passes through a pollen tube that grows down the style to the ovary, enters the ovule and joins with the egg cell.
You might also like to view...
Four of the five answers listed below are
anthropoids. Select the EXCEPTION.
a. gorilla b. human c. tarsier d. lemur e. monkey
Choose the true statements about the evolution of larval dispersal in marine snails.
A. Cladistics shows that there are more instances of the transition from dispersing to non-dispersing larvae than the reverse. B. Loss of structures in the transition from dispersing to non-dispersing may inhibit evolutionary reversal. C. Possession of dispersing larvae is the ancestral state in snails. D. The evolution of non-dispersing snails is likely to hinder speciation. E. Clades of non-dispersing snails are less species rich than those of dispersing snails.
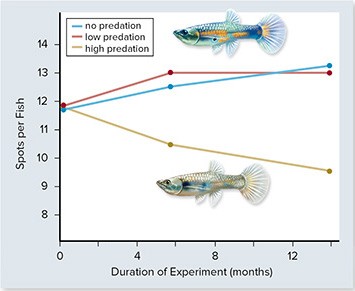 In the experiment above, guppy color patterns (spots) were measured in populations exposed to increasing amounts of predation. From this you could conclude that ________.
In the experiment above, guppy color patterns (spots) were measured in populations exposed to increasing amounts of predation. From this you could conclude that ________.
A. evolutionary changes take millions of years to appear B. brightly colored guppies are more likely to reproduce in the presence of predators C. predators are more likely to catch and eat brightly colored guppies D. predators do not affect the color patterns of guppies E. predators are less likely to catch and eat brightly colored guppies
Which of the following is a relationship between organisms that cannot evolve into a mutualistic relation-ship?
a. parasite–host interaction b. predator–prey interaction c. neutral interaction d. none; any interaction can serve as a precursor